Sensation and Perception in Psychology: Theories and Processes
Document from University about Sensation & Perception. The Pdf explores the concepts of sensation and perception in psychology, providing an overview of theories and processes involved. It includes sections on sensory thresholds, principles of perception, and analysis of senses like hearing, smell, taste, touch, and kinesthesia, useful for University Psychology students.
See more9 Pages
Unlock the full PDF for free
Sign up to get full access to the document and start transforming it with AI.
Preview
Sensation and Perception Unit Overview
Psychologist study sensation and perception to explain how and why externally gathered sensations and perceptions impact behaviors and mental processes. Using input from several anatomical structures, the sensations we perceive process and interpret information about the environment around us and our place within it. This results in perceptions that influence how we think and behave. In this way, sensation and perception provide a bridge between the biological and cognitive perspectives, offering aspects of both for explaining how we think an behave.
** Adapted from College Board's AP Psychology Course and Exam Description **
Defining Sensation and Perception
Define
Sensation: Perception:
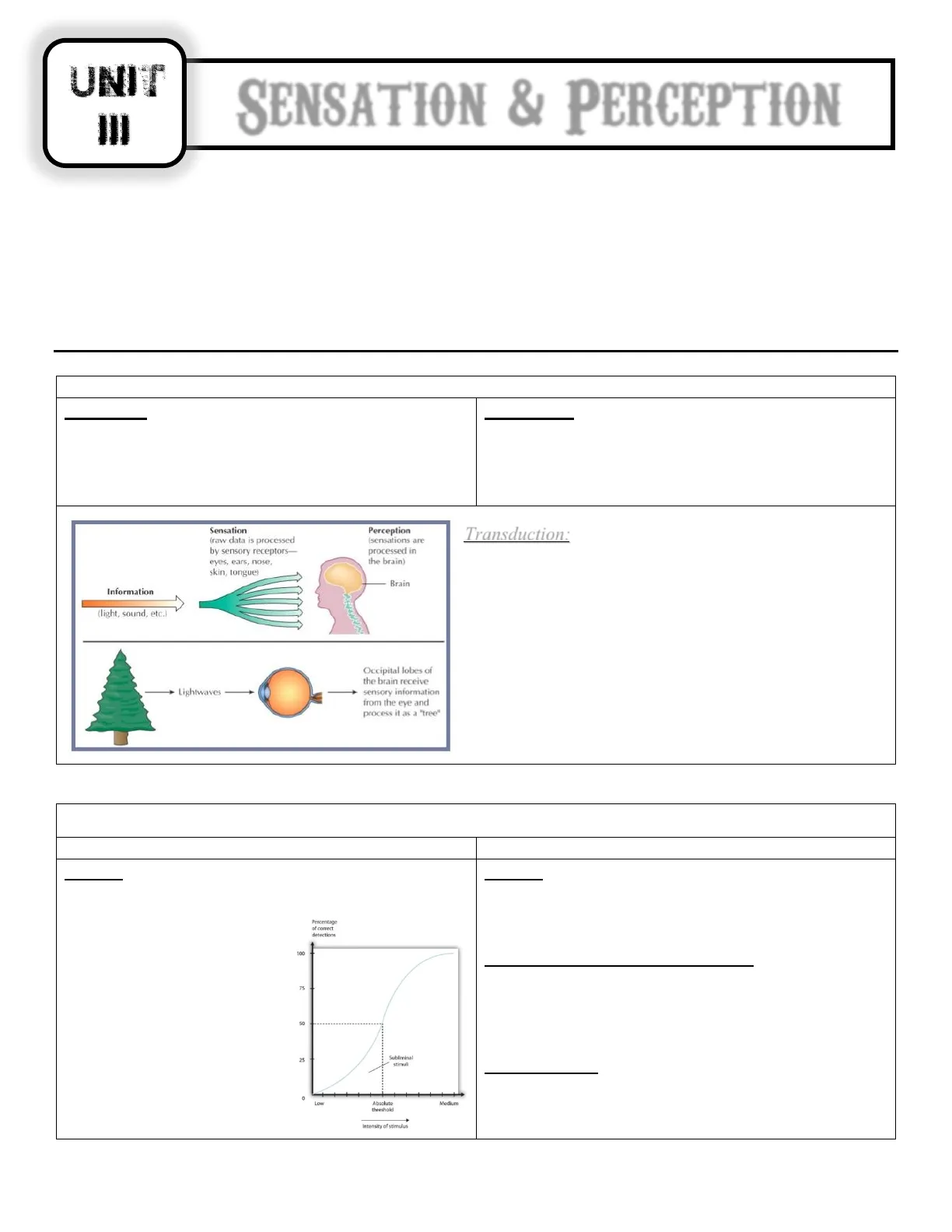
Sensation (raw data is processed by sensory receptors- eyes, ears, nose, skin, tongue)
Perception (sensations are processed in the brain)
Brain Information (light, sound, etc.)
Occipital lobes of the brain receive sensory information from the eye and process it as a "tree"
Principles of Sensation
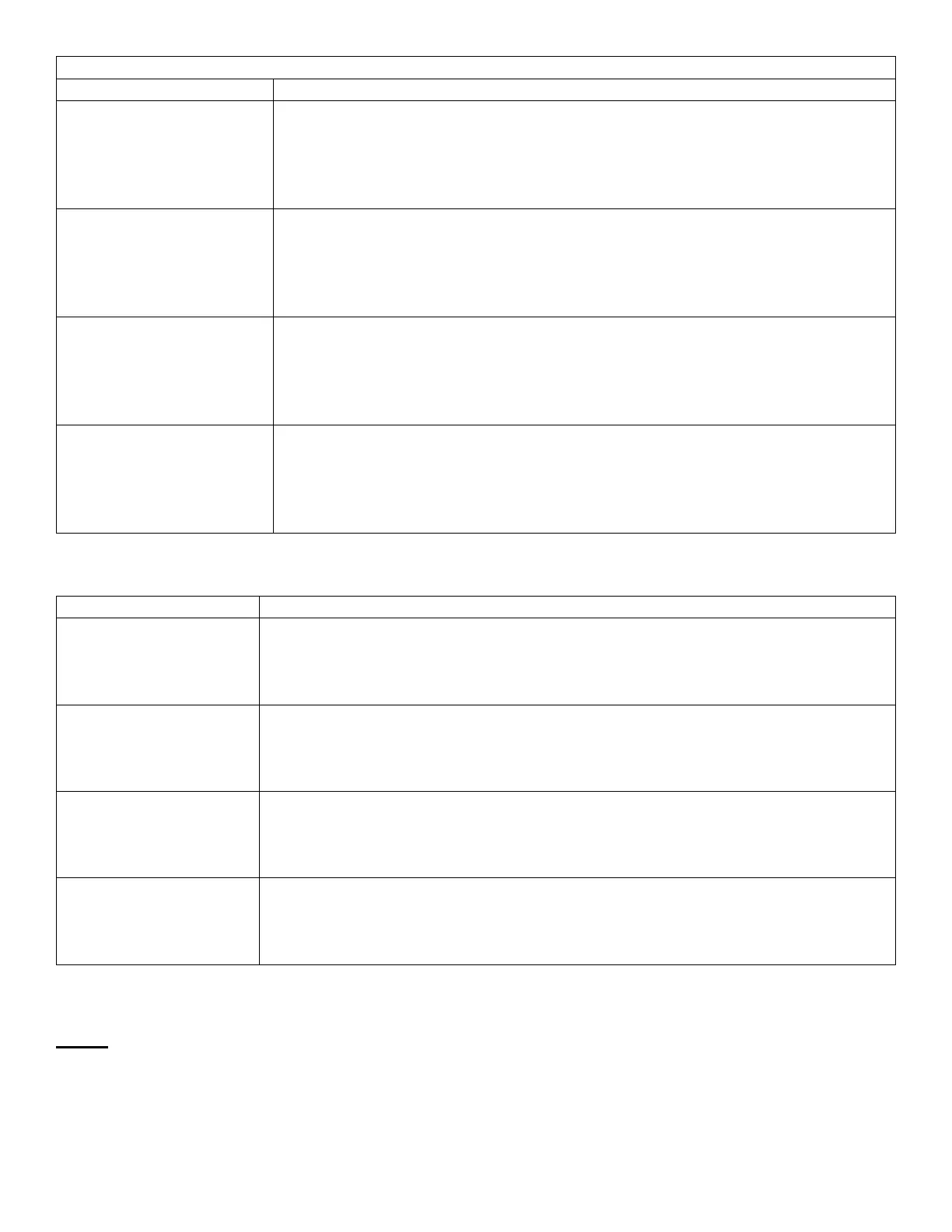
Sensory Thresholds
Absolute Threshold
Define:
Percentage of correct detections 100 75 50 25 Subliminal stimuli 0 Low Absolute threshold Medium Intensity of stimulus
Difference Threshold
Define: Just Noticeable Difference (JND): Weber's Law: Transduction: - Lightwaves -Additional Principles
| Principle | Definition |
|---|---|
| Selective Attention | |
| Signal-Detection Theory | |
| Cocktail Party Effect | |
| Sensory Adaptation |
Principles of Perception
| Principle | Definition |
|---|---|
| Perceptual Set | |
| Context Effect | |
| Bottom-Up Processing | |
| Top-Down Processing |
Gestalt Psychology
Define Gestalt Psychology:
Define Gestalt:
Gestalt Principles of Organization
Similarity Closure Good Continuation Proximity
Define: Define: Define: Define:
Figure-Ground Relationship
Define: What do you see in this ancient pottery? Is it the face of a man or a crane?
Depth Perception
Differentiate between monocular and binocular cues
Monocular Cues: Binocular Cues:
Monocular Cues of Depth Perception
Identify Eight Monocular Cues of Depth Perception Can you identify four monocular cues in the image provided?
Binocular Cues
Retinal Disparity Convergence
Define: Define:
Perceptual Constancies
Size Constancy Shape Constancy
Define: Define:
O O
The Human Senses
| Sense | Notes |
|---|---|
Vision
Label: Fill in the blanks to the eye diagram provided: Vitreous humor
Function: What are the functions of the following parts of the eye? Rods: Cones: Ganglion Cells: Bipolar Cells:
Theories of Vision
Explain the following theories of vision: Trichromatic Theory of Color: Opponent Process Theory of Color: After Image:
Vision Area of the Brain
Which areas of the brain are involved with this sense?
Vision Sensory Disorders
Identify sensory disorders involved with this sense.
Hearing
Label: Fill in the blanks to the eye diagram provided & divide & label the ear diagram to show the outer ear, middle ear & inner ear. pinna malleus incus stapes semicircular canals external ear 12 eustachian tube bone internal carotid artery
Function: What are the functions of the following parts of the ear? Basilar Membrane: Hair Cells:
Theory of Hearing
Explain the following theory of hearing Frequency Theory: Place Theory:
Hearing Area of the Brain
Which areas of the brain are involved with this sense?
Hearing Sensory Disorders
Identify sensory disorders involved with this sense.
Smell
Function: What are the functions of the following parts of smell? Olfaction: Pheromones: Olfactory Bulb:
Smell Area of the Brain
Which areas of the brain are involved with this sense?
Taste
Function: What is the function of the following part of taste? Taste Buds:
Identify: Identify the 5 main tastes What is Umami?
Taste Area of the Brain
Which areas of the brain are involved with this sense?
Touch
Define: Define the following term Pain:
Function: What are the functions of the following parts of touch/pain? Nociceptors: Substance P: Gate Control Theory:
Touch Area of the Brain
Which areas of the brain are involved with this sense?
Kinesthesia
Define: Define the following term: Kinesthetic Sense: Proprioceptors:
Kinesthesia Area of the Brain
Which areas of the brain are involved with this sense?
Vestibular
Define: Define the following term: Vestibular Sense:
Unit Progress Check
Sensation and Perception Learning Objectives
I CAN ...
- Describe general principles of organizing and integrating sensations (gestalt, depth perception, top-down & bottom-up processing) as well as principles of sensory transduction (absolute & difference threshold, signal detection, sensory adaptation).
- Discuss how experience and culture can influence the perceptual process (perceptual set, context effects, schema)
- Describe the vision and hearing process, including the specific nature of energy transduction and relevant anatomical processes, as well as common sensory conditions.
- Describe taste and smell processes, including energy transduction, relevant anatomical structures and pathways to the brain.
- Describe sensory processes, including energy transduction, relevant anatomical structures and pathways to the brain, of each of the body senses (touch, pain, vestibular, kinesthesis).