Financial Statements' Relationships and Accounting Principles
Slides from Alberti 1 about Financial Statements' Relationships and Accounting Principles. The Pdf covers the relationships between financial statements and accounting principles, including learning objectives and detailed explanations. It is suitable for university-level study in Economics.
See more11 Pages
Unlock the full PDF for free
Sign up to get full access to the document and start transforming it with AI.
Preview
ACCOUNTING
Class 5 - 30 September 2023
13.00-16.00 ALBERTI 1 Prof. Federica Farneti
Learning Objectives
- Explain Financial Statement Relationships
- Explain the meaning and usefulness of the accounting equation.
- Explain the meaning of each of the captions on the financial statements illustrated in this chapter.
- Identify and explain the broad, generally accepted concepts and principles that apply to the accounting process.
- Discuss why investors must carefully consider cash flow information in conjunction with accrual accounting results.
- Identify and explain several limitations of financial statements.
- Describe what a corporation' s annual report is and why it is issued.
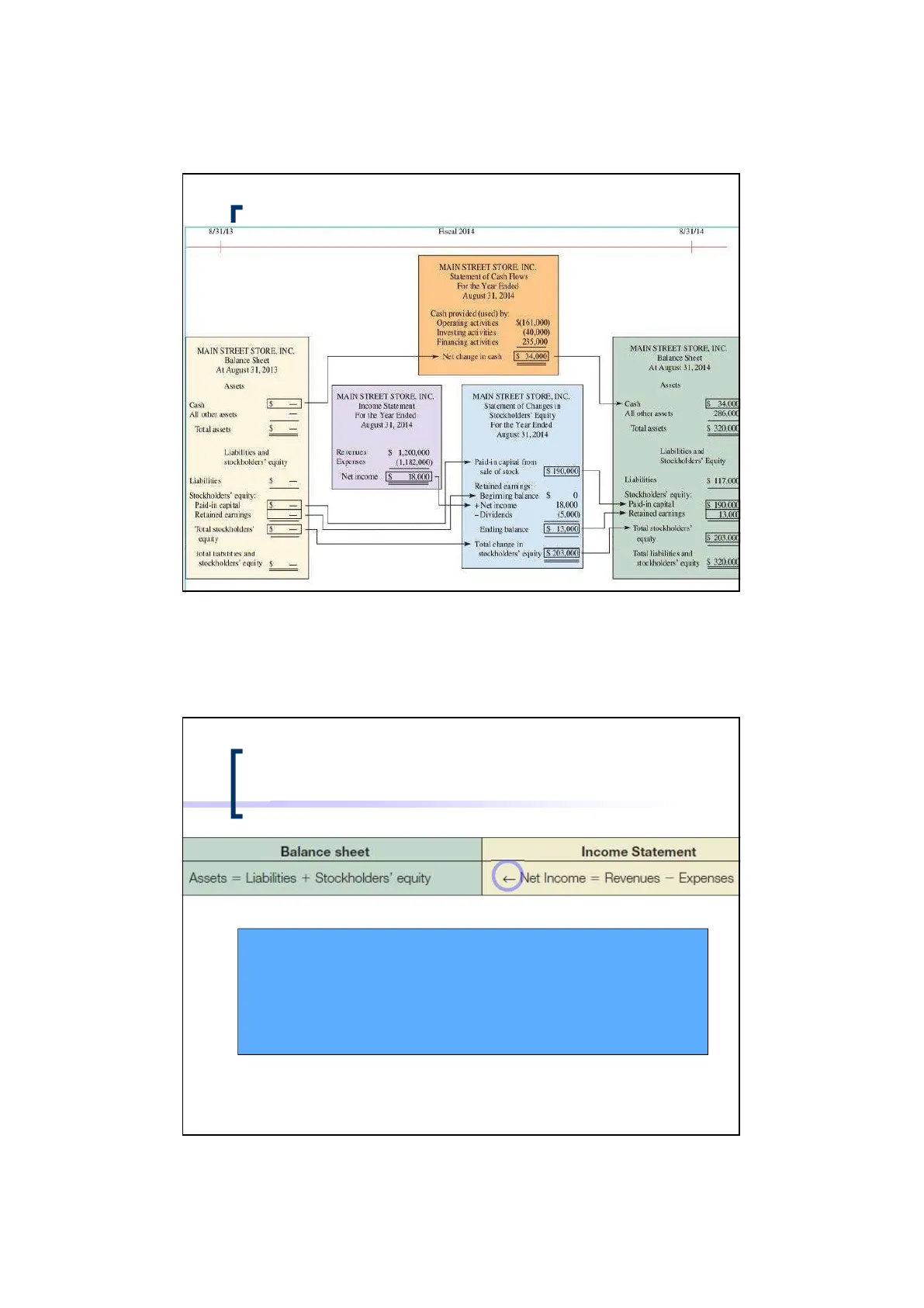
Financial Statement Relationships
r 8/31/14 8/31/13 Fiscal 2014
MAIN STREET STORE, INC. Statement of Cash Flows
For the Year Ended August 31, 2014
Cash provided (used) by: Operating activities Investing activities Financing activities
$(161,000) (40,000) 235.000
Net change in cash $ 34.000
MAIN STREET STORE, INC. Balance Sheet
At August 31, 2014
Assets Assets Cash All other assets S
MAIN STREET STORE, INC. Income Statement
For the Year Ended August 31, 2014
MAIN STREET STORE, INC. > Cash $ 34,000 All other assets 286,000 Total assets $ Total assets $ 320,000
Liabilities and stockholders' equity
Revenues Expenses $ 1,200,000 (1,182,000)
Liabilities and Stockholders' Equity Liabilities S Retained earnings: 0 Stockholders' equity: Paid-in capital Stockholders' equity: Paid-in capital Retained earnings $ + + Net income 18,000 (5,000) + Retained earnings $ 190,000 13.000
Total stockholders' equity S Ending balance $ 13.000
Total stockholders' equity $ 203,000
Total liabilities and stockholders' equity $ Total liabilities and stockholders' equity $ 320.000
Financial Statement Relationships
Balance sheet
Assets = Liabilities + Stockholders' equity
Income Statement
Net Income = Revenues - Expenses
The arrow indicates that net income affects retained earnings because net income is a component of stockholders' equity.
2-4 2
Net income $ 18,000 + Paid-in capital from sale of stock $ 190.000
Liabilities $ 117,000
Beginning balance $ - Dividends Total change in stockholders' equity [$ 203,000
MAIN STREET STORE, INC. Balance Sheet
At August 31, 2013
Statement of Changes in Stockholders' Equity
For the Year Ended August 31,2014
Financial Statement Relationships
If assets equal $300,000 and liabilities equal $125,000, what is stockholders' equity?
Balance Sheet
Stockholders' Equity Assets = Liabilities + 300,000 = 125,000 + ? SE= PIC+RE paid-in cap + Ret earn 00+ & and Exp [
Financial Statement Relationships
If assets equal $300,000 and liabilities equal $125,000, what is stockholders' equity?
Balance Sheet
Stockholders' Assets = Liabilities + Equity 300,000 = 125,000 + 175,000
Stockholders' equity equals $175,000 ($300,000 - $125,000)
3 10000 rcentage[
Financial Statement Relationships
Now, suppose that total assets increase $12,000 during the year and total liabilities decrease $3,000 during the year.
Balance Sheet
Assets = Liabilities + Stockholders' Equity 300,000 125,000 175,000 12,000 (3,000) ? 312,000 122,000 ? What is stockholders' equity at the end of the year?
2-7
Financial Statement Relationships
Stockholders' equity must have increased by $15,000. Since stockholders' equity was $175,000 at the beginning of the year, it must be $190,000 at the end of the year.
Balance Sheet
Assets = Liabilities + Stockholders' Equity 300,000 125,000 175,000 12,000 (3,000) 15,000 312,000 122,000 190,000
4r
Balance Sheet Account Definitions
| Account | Definition |
| Cash | Cash in hand and in the bank |
| Accounts receivable | Amounts due from customers |
| Merchandise inventory | Cost of merchandise acquired and not yet sold |
| Equipment | Cost of equipment purchased |
| Accumulated depreciation | Portion of the cost of equipment that is estimated to have been used up in the process of operating the business |
| Short-term debt | Amounts borrowed that will be repaid within one year of the balance sheet date |
| Accounts payable | Amounts due to suppliers |
| Other accrued liabilities | Amounts owed to various creditors |
| Long-term debt | Amounts borrowed from banks or other creditors that will not be repaid within one year from the balance sheet date |
| Stockholders' equity | Residual claim of owners, computed as "assets minus liabilities" |
Income Statement Captions
| Captions | Explanation |
| Net sales | Amount of sales of merchandise to customers, less the amount of customer returns of merchandise |
| Cost of goods sold | Represents the total cost of merchandise removed from inventory and delivered to customers as a result of sales |
| Gross profit | Difference between net sales and cost of goods sold; Represents the seller's maximum amount of "cushion" from which all other expenses of the business must be deducted before it is possible to have net income |
| Selling, general, and administrative expenses | Represents the operating expenses of the entity |
| Income from operations | Represents one of the most important measures of the firm's activities |
| Interest expense | Represents the cost of using borrowed funds |
| Income taxes | Shown after all of the other income statement items have been reported because income taxes are a function of the firm's income before taxes |
| Net income per share of common stock outstanding | A significant item in evaluating the market value of a share of common stock; often referred to as "earnings per share" or EPS |
5
Statement of Changes in Stockholders' Equity Captions
| Captions | Explanation |
| Paid-in capital | Represents the total amount invested in the entity by the stockholders |
| Common stock | When the common stock has a par value, the amount shown for common stock in the financial statements will be the par value multiplied by the number of shares issued. If the common stock does not have a par value, the amount shown for common stock in the financial statements will be the total amount invested by the stockholders. |
| Additional paid-in capital | Difference between the total amount invested by the stockholders and the par value of the stock |
| Retained earnings | Represents the cumulative net income of the entity that has been retained for use in the business |
| Dividends | Distributions of earnings to the stockholders |
Statement of Cash Flows Captions
| Captions | Explanation |
| Cash flows from operating activities | Net income is the starting point for this measure of cash generation |
| Depreciation expense | Added back to net income because it is subtracted to arrive at net income but does not require the use of cash |
| Increase in accounts receivable | Deducted because it reflects sales revenues, included in net income, but not yet received in cash |
| Increase in merchandise inventory | Deducted because cash was spent to acquire the increase in inventory |
| Increase in current liabilities | Added because cash has not yet been paid for the products and services that have been received during the current fiscal period |
| Cash flows from investing activities | Shows the cash sources and uses related to long-lived assets |
| Cash flows from financing activities | Shows the cash sources and uses related to transactions with creditors and stockholders |
6
Principles Related to the Entire Model
Accounting Entity
Every economic entity can be separately identified and accounted for.
Accounting Equation
A=L+SE
Going Concern Concept
The presumption that the entity will continue to operate in the future-it's not being liquidated.
Now Future
Principles Related to Transactions
Unit of Measurement
Only transactions denominated in dollars (currency) are recorded in the accounting records.
Cost Principle
Transactions are recorded at their original cost to the entity as measured in dollars.
Objectivity
The accountants' desire to have a given transaction recorded in the same way in all situations.
7
Principles Related to Bookkeeping Procedures and the Accounting Process
Accounting Period
The period of time selected for reporting results of operations and changes in the financial position.
Matching Concept
All expenses incurred to generate that periods' revenues be deducted from revenues earned.
Principles Related to Bookkeeping Procedures and the Accounting Process
J Revenue recognized at the time of sale Which is when title to the product being sold passes from the seller to the buyer, or when the services involved in the transaction have been performed
Accrual Accounting
Recognizing revenue at the point of sale and recognize expenses when incurred, even though the cash receipt or payment may occur at a different time.
8
Accrual Accounting Vs. Cash Flows
Revenue Recognition -Timing is the Key
| Accrual accounting recognizes: | Cash flow recognizes: |
| Revenue when revenue is earned, at the point of sale of services or products. | Revenue when payment is received for services rendered or products sold. |
| Expenses when they are incurred. | Expenses when they are paid. |
Principles Related to Financial Statements
Consistency
Provides meaningful trend comparisons over several years.
Full Disclosure
Circumstances and events that make a difference to financial statement users should be disclosed.
Materiality
The benefit of increased accuracy should outweigh the cost of achieving increased accuracy.
Conservatism
When in doubt, make judgments and estimates that result in lower profits and asset valuatations.
9
Limitations of Financial Statements
Financial statements report only quantitative economic data. They do not reflect qualitative economic variables, such as the value of the management team or the employees' morale.
How do the terms "quantitative" and "qualitative" differ?
2-19 [
Limitations of Financial Statements
Historical Cost Concept
Assets are usually valued at the cost of the Asset when acquired.
The balance sheet does not report market values or the replacement cost of the assets.
Matching Concept
Estimates are acceptable provided there is a basis for them.
Many estimates are used, such as warranty costs, depreciation, and pension expense.
10
The Corporation' s Annual Report
The annual report is distributed to shareholders (and others).
It contains the financial statements, together with the report of the external auditor' s examination of the financial statements.
It also contains the Management' s Discussion and Analysis (MD&A).
ONIC 7 .CO எல்லை 11