Ancient Rome: History, Origins, and Chronology
Slides about Ancient Rome: History, Origins, and Chronology. The Pdf explores the founding of Rome, pre-Roman populations, and the phases of Roman civilization (Monarchy, Republic, Empire). This Pdf, suitable for middle school history students, includes activities to reinforce learning.
See more23 Pages

Unlock the full PDF for free
Sign up to get full access to the document and start transforming it with AI.
Preview
Origins of Rome
1.1. The Founding of Rome ROME ROME ROME ROME ROME 753 BC (8th Century BC)
Location of Roman Civilization
o The Roman civilisation was originated in the centre of the Italian Peninsula.
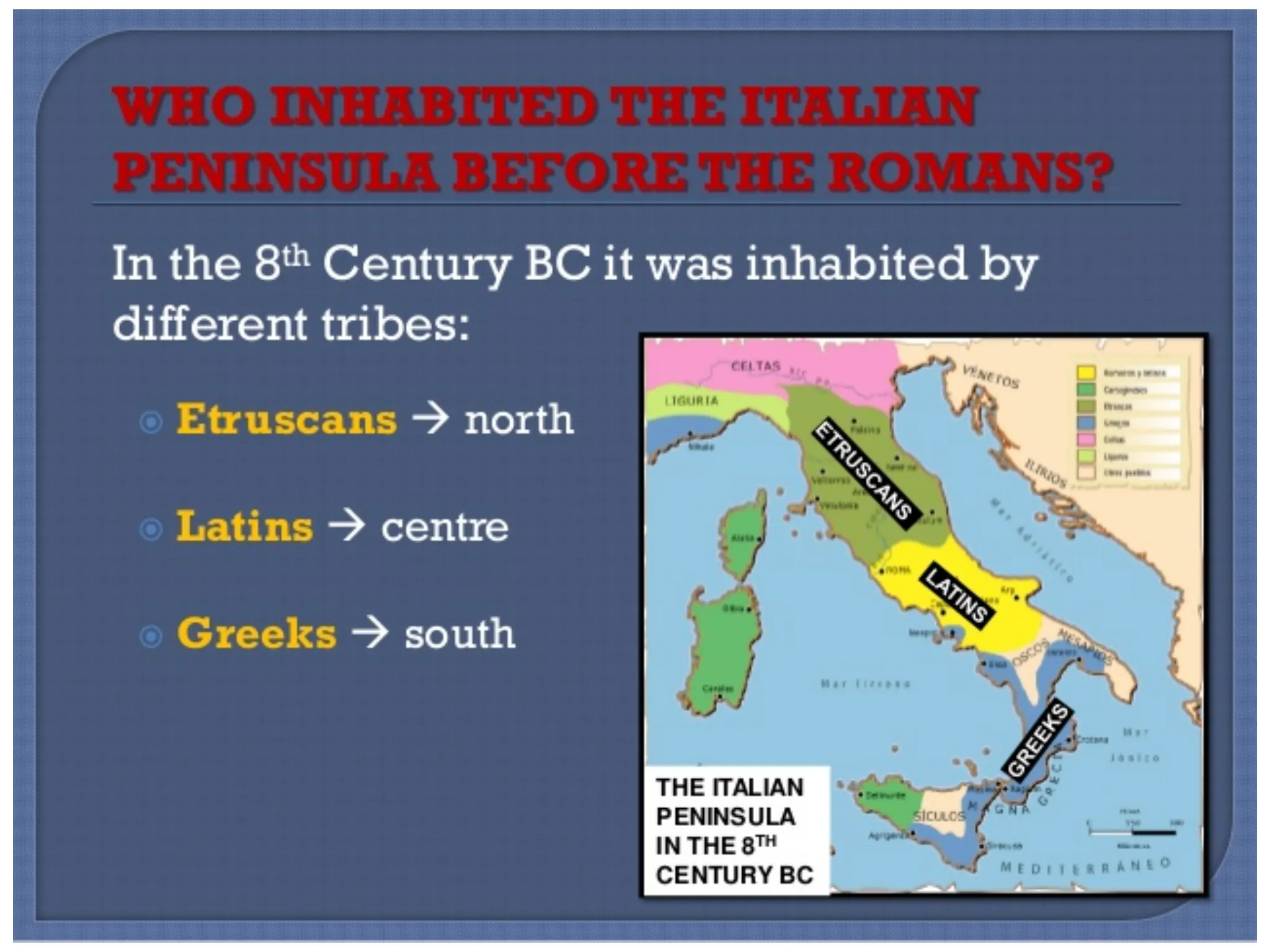
ROME GREECE MESOPOTAMIA EGYPT Mercè JansàWHO INHABITED THE ITALIAN PENINSULA BEFORE THE ROMANS? In the 8th Century BC it was inhabited by different tribes:
- Etruscans north
- Latins > centre
- Greeks > south
CELTAS VÉNETOS LIGURIA -- ETRUSCANS RIRIOS LATINS Roscos MESAPIOS Mar Tigress GREEKS GRECI THE ITALIAN PENINSULA IN THE 8TH CENTURY BC MAGNA SICULOS MEDITERRANEO
Activity 1: Origins of Rome
a) In which Peninsula did the Roman Civilization originated? b) Which were the 3 main tribes that inhabited it in the 8th Century BC? Draw a map locating them in it.
CELTAS VÉNETOS LIGURIA ILIRIOS LATINS MESAPIOS Mar Fireşsa THE ITALIAN PENINSULA IN THE 8TH CENTURY BC Crotona lasico GRECI MAGNA SICULOS MEDITERRANEO ETRUSCANS Ara "loscos GREEKS
Founding of Rome
The origins of Rome are not clear. It's a mix of ...
- Facts -> archaeological remains and ancient texts.
- Legend -> twins Romulus & Remus.
- ACCORDING TO FACTS: Rome was founded in the mid-8th century BC by Latin tribes that settled in 7 hills near the river Tiber.
Tiber River (Tiberis)
CELTAS FUE VÉNETOS Ompos LIGURIA . S ETAU BLIRIOS -- Field of Mars (Campus Martius) Viminal In (Cells Viminalis) LATINS Capitoline Hill (Collis Capitolinus) Esquiline Hell (Collis Esquilinus) Tiber Island (Insula Tiberina Palatine Hull (Callis Palatinus! Caelion Hill (Colis Caeliusi GREEK ... S ...... Aventine Hill (Colis Aventinus) Servian Wall (Murus Servil Tulii) SICIAO MEDITERRANEO
- ACCORDING TO THE LEGEND: Rome was founded in 753 BC by the twin brothers Romulus & Remus, in the place where they were found by the she-wolf. Its name comes from Romulus, who killed his brother and became the first king of Rome.
Activity 2: Founding of Rome Questions
1) According to historical facts, what's the origin of Rome? 2) According to the legend, what's the origin of Rome?
GREC THE ITALIAN PENINSULA IN THE 8TH CENTURY BC Vatican Quirinal Hill (Collis Quirinalis) ETRUSCAN
Chronology of Roman Civilization
The Roman Civilisation went through 3 periods:
Monarchy 753 BC - 509 BC Republic 509 BC - 27 BC Empire 27 BC - 476 AD
Activity 3: Historical Periods Chart
HISTORICAL PERIODS OF ANCIENT ROMAN CIVILISATION
Period Chronology
The Monarchy Period
U1. The monarchy
- Chronology: 753 - 509 BC.
- Form of government: Absolute monarchy. . There were 7 kings in total: . 4 Latin kings · 3 Etruscan kings
- End: in 509 BC the Patricians organised a revolt against the king Tarquin the Proud: . Tarquin the Proud was expelled. . A new form of government was established: the REPUBLIC.
Political Changes: The Republican Government
a) POLITICAL CHANGES: the Republican form of government: Now power was divided among three institutions:
- COMITIA
- SENATE
- MAGISTRATES
The Republic Period (509 - 27 BC)
The main characteristics of this period are:
a) Political changes: the form of government of Rome changed. It became a REPUBLIC. b) Territorial expansion:
509 BC 19 BC
Comitia, Senate, and Magistrates
COMITIA
- All Roman citizens.
- Functions: · Passed laws. · Elected the magistrates.
MAGISTRATES
- Elected annually: · Consul (army) · Aedile (police) · Praetor (justice) · Quaestor (taxes) de las frangas · Censor (list of citizens) · Plebeian tribune (defense of plebeians rights).
- Functions: . Governed Rome.
SENATE
- 300 former magistrates.
- Functions: . Approved laws that had been previously passed by the Comitia. · Controlled the magistrates · Decided on foreign policy.
Dirge jefe de la Edi. Administración markpil Constor Se ocupa Cursor REPUBLIC ROME MONARCHY
Fight for Political Rights
o At the beginning only the patricians had political rights. Plebeian o The plebeians fought during 200 years to have the same political rights. Examples:
- 494 BC: They achieved the right to have a magistrate that defended their interests, the Plebeian Tribune.
- 449 BC: They achieved a written law code, the Twelve Tables.
o In the 3rd Century BC they finally achieved the same political rights as the patricians.
Plebeian Tribune and Twelve Tables
PLEBEIAN TRIBUNE (magistrate that defended the interests of the Plebeians).
Plebeians achieved to have this representative in 494 AC, after a kind of strike ("secessio plebis") in which they abandoned Rome and threaten with founding their own city. They emptied & paralyzed Rome !!
Veto C
Activity 5: Second Period of Rome Questions
1) What form of government was established in 509 BC after the Absolute Monarchy? 2) In this form of government, who had the power? 3) Who elected the magistrates of Rome? Say which magistrate ... · Administered justice? . Controlled the army? . Was in charge of the police? . Made the list of citizens of Rome? · Defended the plebeians interests? · Collected the taxes? 4) Did patricians and plebeians had the same political rights during all the Republic? Explain it.
The Twelve Tables of Rome (449 BC)
By publishing the laws in the Forum all Romans could read and know them, so plebeians were freed from injustice during trials.
Territorial Expansion During the Republic
b) TERRITORIAL EXPANSION:
- During the Republic Rome began to expand territorially.
- This expansion was possible thanks to a very disciplined & organized army.
- PHASES OF THE EXPANSION: · 1°) Italian Peninsula. · 2º) Western Mediterranean. This was achieved by defeating Carthage in the Punic wars. · 3º) Eastern Mediterranean. This was achieved by defeating the Hellenistic Monarchies.
With the final conquests of Egypt (30 BC) and Hispania (19 BC) the Romans controlled all the Mediterranean area which they called "Mare Nostrum" (our sea).
Phases of Roman Expansion
1st ) Domination over all the Italian Peninsula 270 BC
The Western Mediterranean 264 RC Gauis -Carthaginian Empire -Rawas Replic & Allies Carsica ·- Capital Capas Soleork Sardinia Ses Mediterranean Iberians Sea Neva Skelly Syracuse Gadit- Tal Atlantic Ocean Numidians Tings
1ª Punic War (264 - 241 BC)
MAR CANTÁBRICO ILIRIA Pirineos ITALIA CÓRCEGA Roma Cau CERDEÑA Coutora SICILIAP Gracias Agrigento Cartago NUMIDIA MAURETANIA Roma y aliados Cartago
3rd Punic War (149 - 146 BC)
2nd ) Control of the Western Mediterranean These conquests involved 3 wars against Carthage: the PUNIC WARS.
140 BC
3rd) Control of the Eastern Mediterranean After defeating the Hellenistic Monarchies and conquering Egypt (30 BC) and Hispania (19 BC) the Romans controlled all the Mediterranean area which they called "MARE NOSTRUM".
Video about the Punic Wars
YA PYRENEES Ceitiberian's MEDITERRANEAN NUMIDIA SEA MAURETANIA Porng on ! Cartage ( 16 Beginning of the Second Fonic Wor 1218 8℃) Roman dominiann ant sites Compaginion doninvane ant se en
2nd Punic War (218 - 201 BC)
MAR MEDITERRÁNEO Marsil Hippe Regio Cartagono Lapin Magra Carthage Alpes 19 BC
Consequences of Roman Expansion
· CONSEQUENCES OF THE EXPANSION: POSITIVES It provided:
- Raw materials
- Land
- People
NEGATIVES It caused: . Social conflicts: due to the unequal distribution of wealth. Peasants who left their lands to serve in the army couldn't compete with large landowners who's lands were worked by slaves, so they were ruined. . A political crisis: to solve the social conflicts, the Senate gave the power to military chiefs, who fought for absolute power in Civil Wars. In 48 BC Julius Caesar was made dictator for life, but he was murdered in the Senate (44 BC). A new civil war started that led to the end of the Republic in 27 BC.
Activity 6: Second Period of Rome Expansion Questions
5) Explain the phases of the territorial expansion of Rome during the Republic. 6) Who fought in the Punic Wars? Who won? What territorial changes did they brought? 7) What were the consequences of the territorial expansion? 8) Who was Julius Caesar? What happened after his death?
The Empire Period (27 BC - 476 AD)
The main characteristics of this period are:
a) Political changes > Rome became an EMPIRE. b) Historical evolution:
Pax Romana (1st - 2nd Cent) Decline of the Roman Empire (3 - 5th Cent.)
- Crisis of the 3rd century
- Division of the Empire (395)
- Fall of the Western Roman Empire (476)
- 476 395 AD 117 AD
Political Changes: Rise of the Empire
a Political Changes:
- After Julius Caesar's death (44 BC), a civil war started (Octavian Augustus VS Marc Antony).
- 27 BC: Octavian Augustus won, and he was granted complete power establishing a new form of government: the Empire.
- The emperor hold all the power: he summoned the Senate, passed the laws, appointed the magistrates ...
- The Republic's institutions continued to exist, but under control of the emperor.
Historical Evolution: Pax Romana and Romanisation
PAX ROMANA
b Historical evolution:
- 1- 2nd Centuries: period known as PAX ROMANA: o Maximum expansion of Rome o Peace inside Roman frontiers o Division into provinces ruled by governors to make it easier to control such a huge territory. o Romanisation: process through which the conquered people (Barbarians) assimilated the Roman culture (Latin language, art, towns ... )
Romanisation of the conquered people : they adopted Roman language (Latin), art, urbanism ...
M.FILSEVEROPIO CO.PONTIFICMA ILANTONINOA OPTIMISFOR ESTITVTAM.IN S . VIRTUTIBV 25 NORTE MURALLA PERIMETRAL CARDO (NV-SI BASTIONES DESTE ANFITEATRO TEATRO FORD TERMAS Conducción de aque
Activity 7: Third Period of Rome Questions
1) What happened after Julius Caesar's death? What form of government was established? 2) What is the Pax Romana? 3) What name did the Romans gave to the conquered people? 4) How was the huge territory organized and governed during the empire? 5) What was Romanisation?
Provinces of the Roman Empire
Provinces of the Roman Empire This map is not based on a specific timeframe. Sarmatia Europea OCEANUS GALLICUS Lugdunensis Germania Superior Ratia GALLIA Noricum OCEANUS CANTABRIUS - Aquitania Pannonia Daca Taurica Alpina PONTUS EUXINUS Tarraconensis Moesia Italia Corsica Thracia Bahýnia Lusitania Media Macedonia Galatia Cappadocia Assyria Baetica TYRRHENUM Asia Cilicia Mesopotamia HERCULELM Syria Cæsariensis Achasa Creta Cyprus Numidia MARE INTERNUM Judæa Arabia Petraea Arabia Magna Cyrenaica Ægyptus C UNRV.com
Division of the Roman Empire into provinces. They were ruled by governors (proconsul)
ESTIMIE NUM OCEANUS & SUEVICUM GERMANICUS OCEANUS MISE POVICLE Britannia OCEANUS ATLANTICUS Germania Inferior Germania Magna OCEANUA BRITANNICUS Belgica Com Sarmatia Asiatica MARE CASPIM Narbonensis Illyricum MARE NADRIATICUM Pontus Armenia HISPANIA Sardinia Epiru MARE Lycia PRETUM Sicilia) scuLuu Africa MAURETANIA Tingitana