Glándulas Endócrinas: Anatomía e Histología en Biología Universitaria
Diapositivas sobre Glándulas Endócrinas. El Pdf detalla la anatomía e histología de las glándulas endocrinas, como la pineal, pituitaria y paratiroides, con imágenes histológicas de células principales y oxifílicas. Este material de Biología para Universidad explica la función de la PTH y su rol en la regulación del calcio.
Ver más50 páginas

Visualiza gratis el PDF completo
Regístrate para acceder al documento completo y transformarlo con la IA.
Vista previa
Glándulas Endócrinas
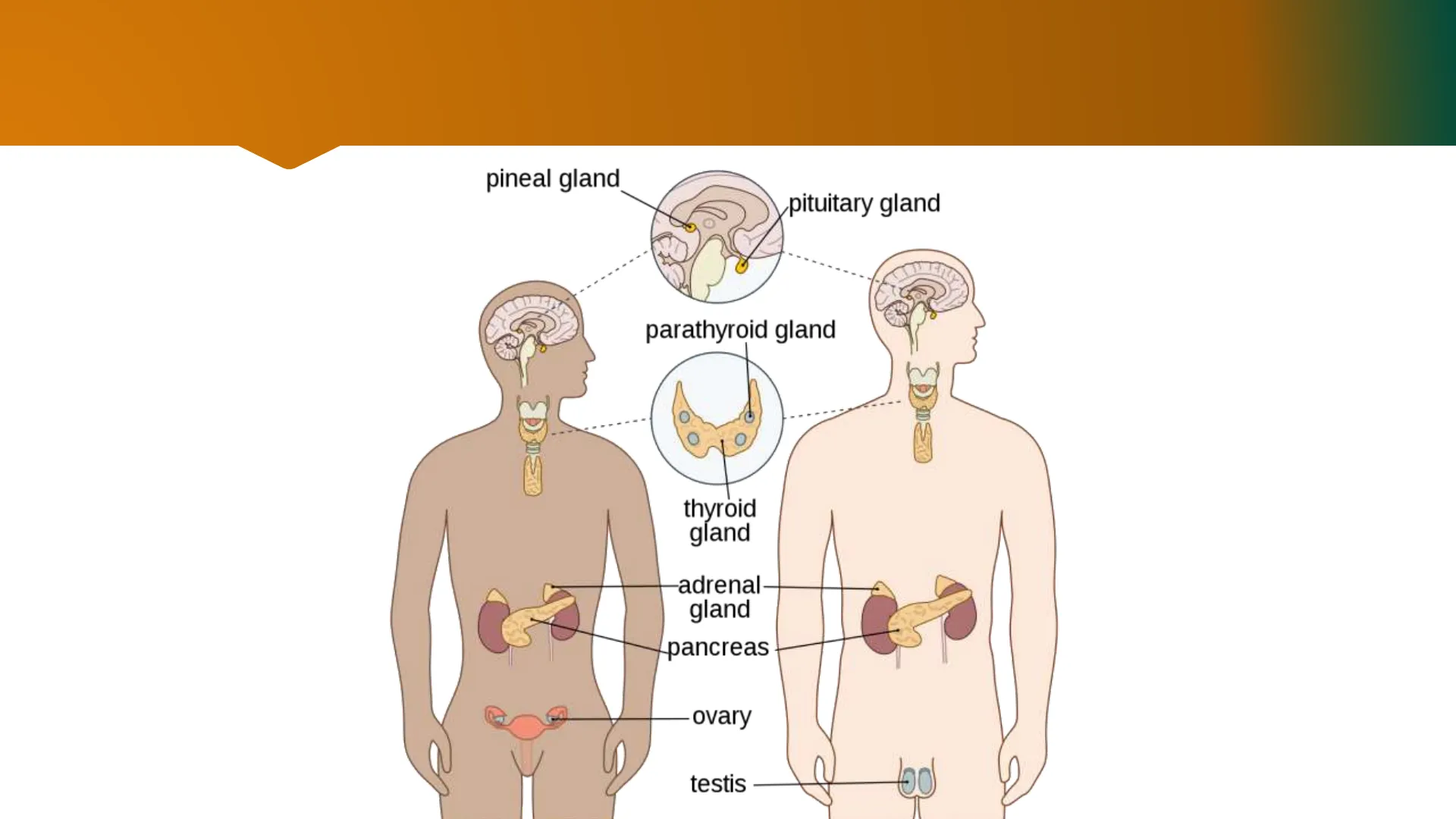
20 .- Glándulas Endócrinaspineal gland pituitary gland parathyroid gland thyroid gland adrenal gland pancreas ovary testis
Tipos de Señalización
- Endócrina: moléculas (hormonas) son transportadas en la sangre hasta la célula blanco
- Paracrina: el ligando se difunde en el líquido extracelular y es metabolizado rápidamente, efecto local, solo en células adyacentes
- Autocrina: el ligando se une a la misma célula que lo produjo
- Yuxtacrina: las moléculas de señalización son proteínas unidas a la membrana celular que se unen a los receptores de superficie de la célula diana cuando las dos células hacen contacto físico directo.
PARACRINE SIGNALING Moooom, he's touching me! Cytolytic T cell (CD8+) Immunologic synapse Interleukin Antigen-presenting cell (macrophage)
Retroalimentación
Glándula Órgano blanco
Hipófisis
- Neurohipófisis
- Derivada del piso del diencéfalo
- Adenohipófisis
- Derivada del techo de la boca
Diencephalon- Neuroectoderm Neurohypophyseal bud Neurohypophyseal bud (future posterior pituitary) Hypophyseal pouch (future anterior pituitary) Hypophyseal pouch Oral ectoderm Pharynx Stomodeum (future mouth) (a) Week 3: Hypophyseal pouch and neurohypophyseal bud form Infundibulum Neurohypophyseal bud Hypophyseal pouch (b) Late second month: Hypophyseal pouch loses contact with roof of pharynx Anterior pituitary Posterior pituitary Median eminence Pars tuboralis Pars intermedia Pars distalis Pars nervosa (c) Fetal period: Anterior and posterior parts of pituitary have formed
Porción tuberosa Infundíbulo Porción media Hendidura intraglandular Porción distal Porción nerviosa
Eje Hipotálamo-Hipófisis
- El hipotálamo se conecta con la neurohipófisis a través del tracto hipotálamo-hipofisiario (axones)
- Núcleo paraventricular: produce oxitocina
- Núcleo Supraóptico: produce ADH
- Ambas son almacenadas en la neurohipófisis y después liberadas a los capilares de la arteria hipofisiaria inferior
Pituicito Cuerpo neurosecretor 50 um
Adenohipófisis
Los componentes principales son cordones de células endocrinas intercaladas con capilares fenestrados y tejido conectivo reticular de soporte
Células Cromófilas
- Acidófilas
- Somatotropas (somatotropina)
- Son las más abundantes
- Lactotropas (prolactina)
- Basófilas
- Corticotropas (ACTH)
- Tirotropas (TSH)
- Menos abundantes
- Gonadotropas (FSH, LH)
- Células cromófobas
GH PRL ACTH TSH FSH LH60 μm70 μm60 μm5a GH PRL c TSH d'CH e FSH ACTH
Porción Intermedia
Quistes de Rathke 200 μm
Hypothalamus Anterior Pituitary Posterior Pituitary Cortisol ACTH ADH Kidney Water Absorption Oxytocin T4, T3 Thyroid Uterus -> Contraction Inhibin FSH Prolactin Mammary Gland Milk Production and Secretion Testosterone LH Estrogen FSH GH Ovary Bone -> Growth Progesterone LH (IGF-1) Adrenal Cortex TSH Testis
Tipos Celulares y Hormonas Producidas
Cell Type % of Total Cells Hormone Produced Major Function Somatotrophs 50 Somatotropin (growth hormone, GH), a 22-kDa protein Stimulates growth in epiphyseal plates of long bones via insulin-like growth factors (IGFs) produced in liver Lactotrophs (or mammotrophs) 15-20 Prolactin (PRL), a 22.5-kDa protein Promotes milk secretion Gonadotrophs 10 Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH; interstitial cell- stimulating hormone [ICSH] in men), both 28-kDa glycoprotein dimers, secreted from the same cell type FSH promotes ovarian follicle development and estrogen secretion in women and spermatogenesis in men; LH promotes ovarian follicle maturation and progesterone secretion in women and interstitial cell androgen secretion in men Thyrotrophs 5 Thyrotropin (TSH), a 28-kDa glycoprotein dimer Stimulates thyroid hormone synthesis, storage, and liberation Corticotrophs 15-20 Adrenal corticotropin (ACTH), a 4-kDa polypeptide Lipotropin (LPH) Stimulates secretion of adrenal cortex hormones Helps regulate lipid metabolism
Control de Secreción Hormonal
Hypothalamus Regulatory hormones of hypothalamus Tropic hormones of anterior pituitary Releasing hormones: TRH, PRH, GnRH, CRH, GHRH Inhibiting hormones: PIH, GIH Infundibulum Anterior pituitary --- Posterior pituitary Muscle TSH GH Growth hormone (GH) acts on all body tissues, especially cartilage, bone, muscle, and adipose connective tissue to stimulate growth. Thyroid Bone Adipose connective tissue PRL Mammary gland -Adrenal cortex ACTH Prolactin (PRL) acts on mammary glands to stimulate milk production. FSH and LH Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH) act on gonads (testes and ovaries) to stimulate development of gametes (sperm and oocyte). Testis Ovary · Las actividades de las células de la hipófisis anterior están controladas principalmente por hipotalámicas hormonas relacionadas con péptidos producidas por pequeñas neuronas del cerca tercer ventrículo, descargadas desde los axones en la eminencia media y transportadas por los capilares del sistema portal a través de la hipófisis anterior Hormone Functions Thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) Stimulates release of thyrotropin (TSH) Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) Stimulates the release of both follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH) Somatostatin Inhibits release of both somatotropin (GH) and TSH Growth hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH) Stimulates release of GH Dopamine Inhibits release of prolactin (PRL) Corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) Stimulates synthesis of pro-opiomelanocortin (POMC) and release of both @-lipotropic hormone (B-LPH) and corticotropin (ACTH) Adrenal gland Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) acts on the adrenal cortex to cause release of corticosteroids (eg, cortisol). Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) stimulates the thyroid gland to release thyroid hormone (TH).
Retroalimentación Negativa
Hypothalamus 1) A stimulus (eg, low body temperature) causes the hypothalamus to secrete thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH), which acts on the anterior pituitary. -stimulatory -inhibitory Negative feedback inhibition TRH 5) Increased body temperature is detected by the hypothalamus, and secretion of TRH by the hypothalamus is inhibited. TH also blocks TRH receptors on the thyrotropic cells, inhibiting synthesis and release of TSH. Both effects indirectly dampen TH production in the thyroid. 2 Thyrotropic cells in the anterior pituitary release thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). Anterior pituitary TSH + Target organs in body TH 4 TH stimulates target cells to increase metabolic activities, resulting in an increase in basal body temperature. 3) TSH stimulates follicular cells of the thyroid gland to release thyroid hormone (TH). Relationship between the hypothalamus, the anterior pituitary, and its target organs is shown, using the thyroid as an example. Hypothalamic thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) stimulates secretion of thyroid-stimulating hormone or thyrotropin (TSH), which stimulates synthesis and secretion of thyroid hormone (TH). In addition to their effects on target organs, TH inhibits TSH secre- tion from the pars distalis and TRH secretion from the hypothala- mus by negative feedback.
Glándula Pineal
- Derivada del neuroectodermo de la pared posterior del tercer ventrículo
- Regula los patrones de sueño al producir melatonina Secreción estimulada por la oscuridad, inhibida por la luz
- Células
- Pinealocitos -> secretan melatonina Células intersticiales gliales > provee soporte estromal
- Cuerpos arenáceos > sales de calcio y magnesio, incrementan con la edad
0 CA d Hyp Pitu
Concept Mapping del Sistema Neuroendocrino
Neuroendocrine System Neuroendocrine system Hypophysis Pineal gland Neurohypophysis Interstitial Pinealocytes cells Melatonin Pars tuberalis Pars distalis Infundibulum Pars nervosa Acidophils Basophils Pituicytes Unmyelinated axons Growth hormone Prolactin Follicle- stimulating hormone (FSH) Lutenizing hormone (LH) Thyrold- stimulating hormone (TSH) Adrenocortico- tropic hormone (ACTH) Adrenal cortex Liver Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) I Lactating mammary gland Granulosa cells (ovaries) Sertoli cells (testes) Corpus luteum (ovaries) Leydig cells (testes) Follicular cells (thyroid) Zona fasciculata Zona reticularis Neurophysin Oxytocin or (carrier) Antidiuretic hormone Collecting tubule (kidneys) Myometrium (labor) Myoepithelial cell (lactation) Hormonal targets Hormonal targets Oxytocin Antidiuretic hormone Paraventricular nucleus Supraoptic nucleus Hypothalamus ona r Osteoblasts Adenohypophysis Gonadotropins
Glándulas Suprarrenales
- 2 porciones endócrinas
- Corteza: derivada del mesodermo
- Médula: derivada del neuroectodermo
Right and left inferior phrenic arteries Inferior vena cava Piramidal Right adrenal gland Semilunar Left adrenal gland Right adrenal vein Left inferior phrenic vein Left inferior adrenal artery Right renal artery and vein Left adrenal vein Left kidney Left renal artery and vein A Inferior vena cava Abdominal aorta
Connective tissue- capsule Adrenal gland Cortex Medulla Superior surface of kidney
Hormonas Liberadas por Tejido
Tissue area Hormones released Examples Zona glomerulosa (adrenal cortex) Mineralcorticoids (regulate mineral balance) Aldosterone - Zona fasciculata (adrenal cortex) - Glucocorticoids (regulate glucose metabolism) Cortisol Corticosterone Cortisone - Zona reticularis (adrenal cortex) Androgens (stimulate masculinization) Dehydroepian- drosterone Adrenal medulla Stress hormones (stimulate sympathetic ANS) Epinephrine Norepinephrine
Zona Glomerular
300 um Zona Glomerular · 15% de la corteza · Cordones redondeados o arqueados de células de citoplasma claro · Secretan mineralocorticoides (afectan la recaptación de Na+, K+ y agua en los túbulos renales) Ej. Aldosterona
Zona Fasciculada
300 um Zona Fasciculada · 65% - 80% de la corteza · Células poliédricas, con citoplasma vacuolado dispuesto en cordones de 1 a 2 células de grosor, separados por capilares fenestrados · Secretan glucocorticoides (afectan el metabolismo de carbohidratos; gluconeogénesis y síntesis de glucógeno) ej. Cortisol 0 € e
Zona Reticular
300 um Zona Reticular · 10% de la corteza · Células de menor tamaño, con un citoplasma más eosinofílico y cantidades variables de lipofuscina · Secretan andrógenos ej. DHEA