South Africa History: Facts, Cultures, and Timeline
Document from Study.com about South Africa History: Facts, Cultures & Timeline. The Pdf explores the history, culture, and geography of South Africa, focusing on apartheid and the post-apartheid era, suitable for University-level History students.
See more8 Pages

Unlock the full PDF for free
Sign up to get full access to the document and start transforming it with AI.
Preview
South Africa History Overview
Study.com® Plans Courses v South Africa History | Facts, Cultures & Timeline Author Peter M. Williams View bio Instructor Christopher Muscato View bio You are viewing lesson 16 in chapter 2 of the course: Learn about the history of South Africa, its origins, and its development. View South Africa facts related to its religion, language, and the system of apartheid.
Table of Contents
- South Africa: Overview
- The History of South Africa: Timeline and Major Events
- South Africa: Facts and Culture
- Lesson Summary
South Africa: Overview
There are seven continents in the world. Among these continents is Africa, which is the second-largest continent after Asia. Africa contributes to more than 17 percent of the total world population. Africa has 54 countries, according to the United Nations. Among these countries is South Africa. It is the ninth largest country in Africa. It lies at the southern tip of the African continent, hence the name South Africa. South Africa serves as a tourist attraction site, and also it is recognized for its education system. In addition, industrialization is at a high rate in South Africa. Historically, South Africa was a settlement for the whites during the colonial period.
South Africa's Geography and Location
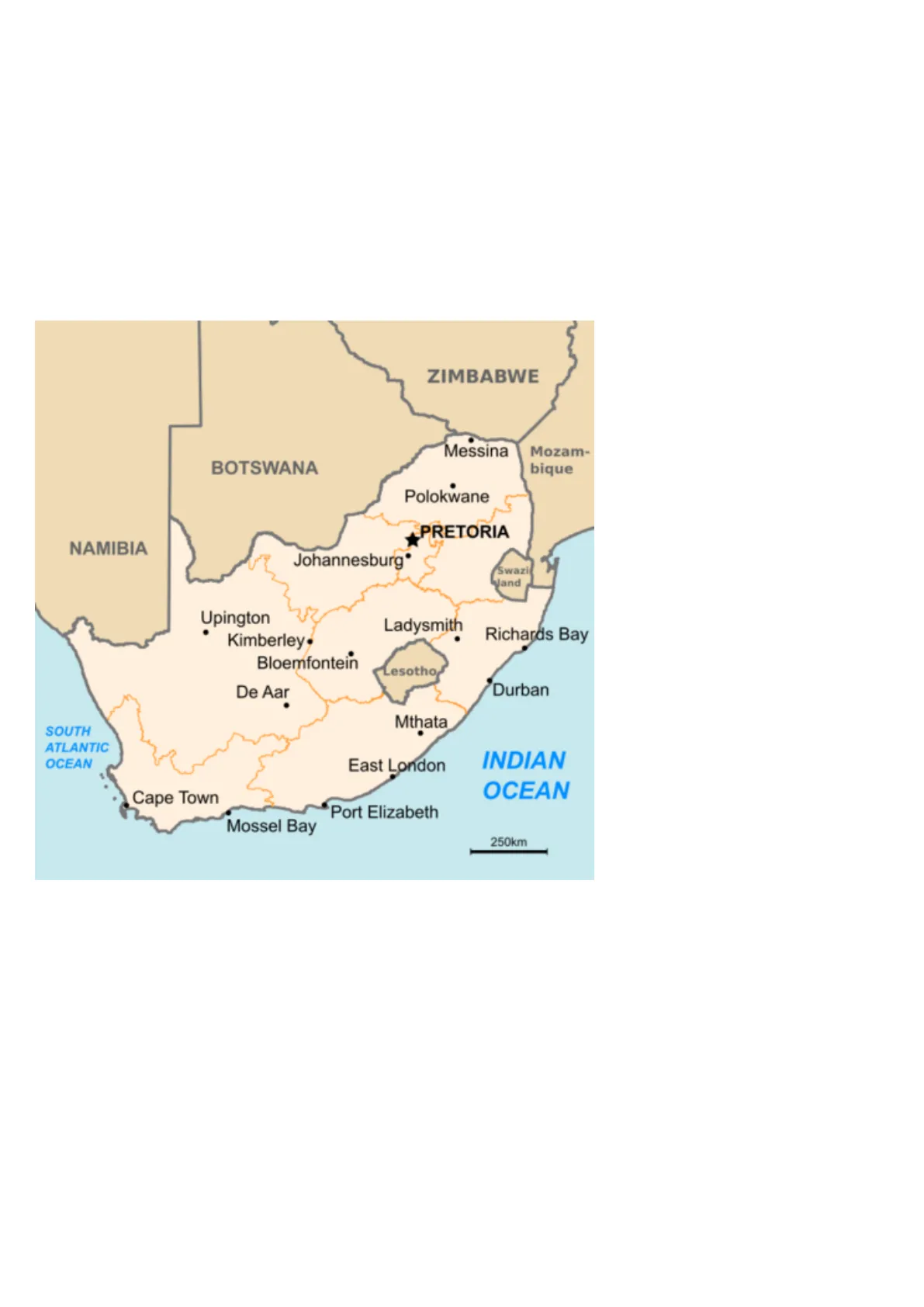
South Africa is located at the southern tip of the African continent. It is bordered by five countries, being Namibia, Botswana, Swaziland, Mozambique, and Zimbabwe. In addition, South Africa encloses entirely the territory of Lesotho, which is a country on its own. South Africa is comprised of nine regions/provinces: Northern Cape, Eastern Cape, Western Cape, Free State, Gauteng Limpopo, North West, KwaZulu-Natal, and Mpumalanga.
ZIMBABWE Messina Mozam- bique BOTSWANA Polokwane PRETORIA NAMIBIA Johannesburg* Swazi vand Upington Ladysmith Richards Bay Kimberley. Bloemfontein Lesotho. Durban De Aar Mthata SOUTH ATLANTIC OCEAN East London INDIAN OCEAN Cape Town Port Elizabeth Mossel Bay 250km The Map Of South Africa
The History of South Africa: Timeline and Major Events
The history of South Africa is is long and diverse. It has several notable events based on the prehistoric period. For instance, during 3,000,000 BCE, South Africa was occupied by australopithecines, also known as Taung Child. This was the earliest hominid closest to the modern man. In addition, South Africa was occupied by the biggest and the most recent australopithecine with robust jaws, skull, and teeth during theMiddle Stone Age period (2,000,000 BCE). This species was called Australopithecus Robustus.
The southern region of Africa (region below DRC Congo and Tanzania) was first occupied by the San people, who were hunters and gatherers during 20,000 BCE . 'Men of men,' mostly known as Khoikhoi, were the first to occupy South Africa, making South Africa one of the world's oldest regions inhabited by modern man. Khoikhoi were pastoralists/cattle keepers, and they coexisted with the San people. The blend between Khoikhoi and San resulted in a group called Khoisan.
Lastly, most of the ancestors of the Bantu-speaking modern population and the mixed farmers settled in the south of River Limpopo during 300 A.D. The Bantu people had migrated from the Northern part of Africa and settled in this region. Trading and exchange of goods were common among these people.
Ancient South Africa
The people in ancient South Africa lived in extended families of less than one hundred and villages of between 500 and 1000 people. These made them live in small chiefdoms with leaders who settled disputes among themselves. The people of ancient South Africa were San, Xhosa, Zulu, Venda, Kalanga, Tsonga, and Sotho. The San has the longest ancestral lineage in South Africa.
The San Has the Longest Ancestral Lineage in South Africa.
One of the ancient cities, Mapungubwe, had its leaders base their power and wealth on the Indian Ocean International Trade. Trading involved goods such as ivory, iron gold, snail shells, ostrich eggshells, and woods. This was a mark of civilization.
The Kingdom of Mapungubwe (10-13th century A.D), was rich in gold, iron, bone tools, and glass beads. When this kingdom declined, the power moved eastwards to Thulamela and the north leading to the emergence of the kingdom of Great Zimbabwe.
South Africa During the Colonial Period
The first European settlers, the Dutch, landed in South Africa in 1652. During this period, the Dutch East India Company was established in Cape of Good Hope, also known as Cape Colony. This region was a Dutch colony but was later overtaken by the British. The Dutch East India Company played an important role in supplying sailors from the Netherlands with fruits and vegetables during colonial times.
After the Dutch settlement in the Cape colony, the British started occupying the region. The British occupation in Cape Colony happened twice, in 1795 and 1806. In 1795, the British took the Cape Colony away from the Dutch. However, the Dutch regained it in 1803 through a treaty. Eventually, Cape Colony was later reconquered by the British in 1806.
Most of the British settlers arrived in the Cape colony in 1820. The British immigrants used condescending terms such as Boers to refer to the earlier settlers (Dutch speakers), meaning farmers. However, the Dutch-speakers had adopted the term Afrikaners (Dutch speakers) as their identity.
The other group of people associated with South Africa during the colonial period was the Portuguese. They were more into trade, and they used the Cape Colony Cape as one of their sea routes. Their ships used to sail mainly to India and East Africa. However, the Portuguese did not establish any settlement in this region.
Conflict in the Nineteenth Century
Between 1811-1812, the Africans occupying the west of the Great Fish River were expelled by the British and the colonial powers. In 1815,there was a rebellion against the British colonial powers by the Boers on the Eastern Cape, commonly known as the Slagtersneck rebellion. In addition, there was a fight between the British Empire and the Dutch settlers called the Boer War.
War also existed among the Africans. For instance, between 1816- 1828, a leader named Shaka formed the Zulu Kingdom that waged war against the Africans along southeastern Africa. This was called the Mfecane war. In 1838, during the Battle of Blood River, the Zulu army was defeated by an Afrikaner commando. In addition, Zulu was also defeated by the British and the colonial powers in 1879.
South Africa's Independence and Apartheid
The Union of South Africa was formed in 1910 by the British empire. It was a union of four republics: Natal, Cape Colony, Transvaal, and Orange Free state. As a member of the British empire, South Africa participated in World War I between 1914-1919.
In 1948, an election was held, and the Afrikaners National Party (also known as National Party) emerged as the winner. This party immediately started to apply its apartheid policy. Apartheid (literally meaning apartness or separation) was a policy that separated people based on their race. However, apartheid was declared a crime against humanity by the United Nations in 1966. As a result, the National Party renounced apartheid in 1990. During this period Nelson Mandela and other political prisoners were released from jail.
South Africa left the British Commonwealth and became an independent republic in 1961. This was after the National Party, led by Hendrik Verwoerd, won a referendum held in 1960 with the aim of making South Africa a republic. Since the issue of apartheid was getting heavily criticized worldwide, the majority of the whites supported this proposal. As a result, South Africa separated itself from the British Commonwealth, and a law was passed declaring it a republic under Verwoerd.
Post-Apartheid South Africa
Apartheid in South Africa came entirely to an end between 1990-1994. In 1994, Nelson Mandela was sworn in as the president of SouthAfrica, with De Klerk as his deputy president. He formed the Government of National Unity. During this period, South Africa rejoined the British commonwealth. In addition, the rates of crimes were intensifying.
In 1996, South Africa enacted a new constitution that gave equal rights to its citizen irrespective of their race and gender.
Nelson Mandela retired in 1999, and Thabo Mbeki became the president of South Africa. During this period, the government employees, including teachers, went on a strike demanding a pay rise. In 2003 South Africa recorded the highest number of people with HIV/AIDS globally.
South Africa: Facts and Culture
South Africa is a home of diversified culture. This diversity was contributed by the early inhabitants such as the Khoikhoi, San, European settlers, and Bantu migrants. Each group brought their unique and blended it with the other groups. As a result, the culture, such as oral traditions and art, was passed from generation to generation. Some of the linguistic groups living in the region include Zulu, Sotho, Ndebele, and Venda.
The Languages of South Africa
South Africa has 11 official languages, with an addition of other minor languages. The Khoisan language is one of the oldest languages in South Africa, characterized by sound clicks. The Bantu migrants also had their languages, including Zulu, Xhosa, Sotho, Pedi, and Tswana. These languages made communication easier, especially during trading.
The white settlers, such as the Dutch, introduced this language to the region, and the Dutch-speaking community was referred to as Afrikaners. These individuals were farmers. The British also introduced the English language during their colonial era.
Currently, the top five languages spoken in South Africa are Zulu, followed by Xhosa, Afrikaans, English, and lastly, Northern Sotho.
The Religions of South Africa
Religion in South Africa is also diverse, with five major religions. Theseare Christianity, Islam, Judaism, Hinduism, and traditional African religion. Except for traditional African religion, these religions were introduced to South Africa by the European settlers. However, the majority of the people of South Africa are Christians.
Most traditional religions believed in deities, ancestral spirits, and magic. For instance, Zulu people worshipped several deities, including Unkulunkulu (the Supreme Deity), uNgungi (blacksmiths deity), Nomhoyi (river goddess), and Sonzwaphi (the healer).
South African Foodways and Music
Before colonization, South African people were cattle keepers, farmers, hunters, and gatherers. Some of the main foods included:
- Milk
- Ostrich eggs
- Meat from tortoises, crayfish, and also cattle.
- Squash
- Insects such as locusts and termites.
- Dried fruits
As the European settled in South Africa, they introduced biscuits, baked goods, spiced meat, wine, fruits, and vegetables (watermelon, pineapples, cucumbers, and potatoes).
The history of South Africa attributes music to the early people. Despite spending time in rock painting, they were also rooted in music. In the 1600s, several musical instruments, such as a four-wired guitar (ramkie) and a one-string violin (mamokhrong), were used by Khoikhoi in their music. Their music was more of polyphonic chants. Some traditional music instruments were flutes, drums, guitar, horns, whistles, and rattles.
Lesson Summary
South Africa is located at the southern tip of the African continent. It is bordered by five countries, being Namibia, Botswana, Swaziland, Mozambique, and Zimbabwe. South Africa is one of the oldest regions to be inhabited globally. During the prehistoric period, South Africa was occupied by australopithecines, Australopithecus Robustus and Khoikhoi. Mapungubwe was one of the ancient cities in South Africa. The people of ancient South Africa were San, Xhosa, Zulu,