Cardiovascular Arrhythmias: Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, and Treatment
Outlines from Ninja Nerd about Cardiovascular Arrhythmias. The Summaries provide detailed schemes on bradyarrhythmias and tachyarrhythmias, including mechanisms and causes. This University-level Biology material is well-structured with tables and diagrams for clear understanding.
See more27 Pages
Unlock the full PDF for free
Sign up to get full access to the document and start transforming it with AI.
Preview
I. Pathophysiology
A. Bradyarrhythmias
1. Pathophysiology:
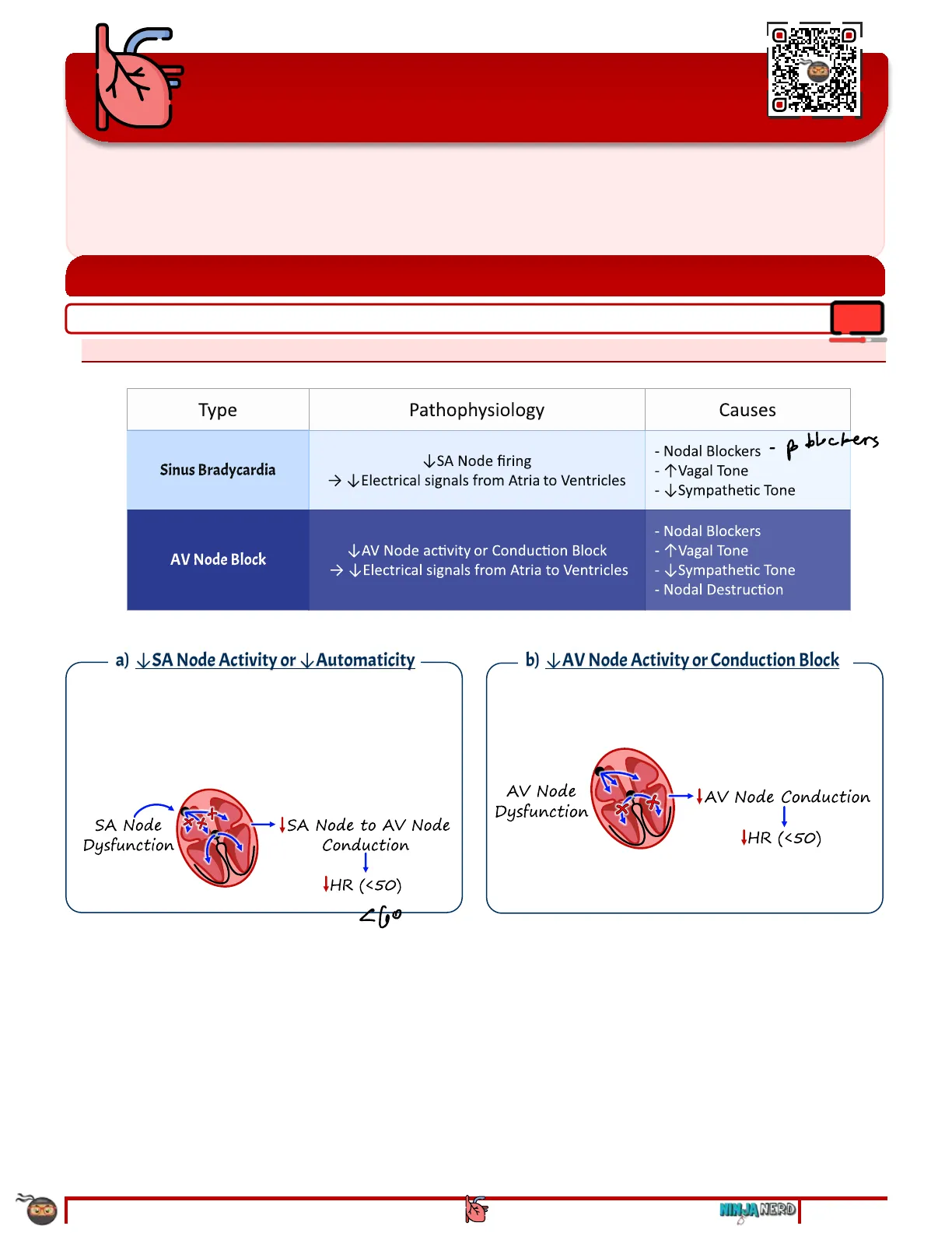
Type Pathophysiology Causes poblockers Sinus Bradycardia VSA Node firing > Electrical signals from Atria to Ventricles - 1 Vagal Tone - Sympathetic Tone - Nodal Blockers - T Vagal Tone AV Node Block AV Node activity or Conduction Block > Electrical signals from Atria to Ventricles - Sympathetic Tone - Nodal Destruction
a) SA Node Activity or \ Automaticity o SA node firing -> \ SA node to AV node conduction -> Electrical signals carried from the atria to the ventricles -> Ventricular depolarization -> Ventricular contraction -> Heart Rate (< 50 bpm) SA Node Dysfunction ISA Node to AV Node Conduction 1 IHR ( < 50 ) 260
b) \ AV Node Activity or Conduction Block o AV node conduction -> \ Electrical signals carried from the atria to the ventricles -> \ Ventricular depolarization -> Ventricular contraction -> \ Heart Rate (< 50 bpm) AV Node Dysfunction - JAV Node Conduction 1 IHR ( < 50 )
B. Tachyarrhythmias
1. Pathophysiology
i) 1 Automaticity o 1 SA Node firing -> ^ SA Node to AV node conduction -> 1Electrical Signals carried from the atria to the ventricles -> 1 Ventricular Depolarization -> ^ Ventricular Contraction -> 1Heart Rate (> 100 bpm) A normal - SATUL fine Y abnormal - altro focus TV tire It Sympathetic Tone - ISA Node Conduction +Beta-1 Receptors IHR -tAV Node - Conduction INE/EPI YY Beta- 1 Receptors Ca++tt Nodal Conductiontt
ii) 1 Re-Entry o Electrical impulses circulating within a loop of cardiac tissue continually stimulate cardiac tissue -> 1 Electrical signals carried from the atria to the ventricles -> ™Ventricular Depolarization -> ^Ventricular Contraction -> o 1 Heart Rate (> 100 bpm) Requires a Premature Stimulus: . 1 Automaticity . 1 Triggered Activity . Types of Anatomical Re-entry: · AVRT · AVNRT IRe-Entry Atrial Re-Entrant Circuits Ventricular Re-Entrant Circuits Atrial Remodelin Ventricular Remodeling 11/2 PILAR ttAtrialtt Stretch 1 ttVentricular Fibrosis/Stretchtt 1 CHF HTN Mitral Stenosis Myocardial CHF (EF< 35%) Infarction
-iii) 1 Triggered Activity o Cardiac tissue undergoes after depolarizations before it has a chance to fully repolarize -> Ectopic action potentials are generated -> ^ Electrical signals carried from the atria to the ventricles -> ^Ventricular Depolarization -> ^Ventricular Contraction -> 1Heart Rate (> 100 bpm) . Early After Depolarization (EAD) . Prolonged QT Interval Delayed After Depolarization (DAD) . 1Calcium Influx tTriggered Activity + tAtrial Ectopy 1 HRt IVentricular Ectopy + HRİ Early after Depolarization Delayed after Depolarization ttQT-Interval 1 ttEAD's It Calcium Influx 1 ttDAD's
II. Complications of Arrhythmias
A. Unstable Arrhythmias
B. Cardiac Arrest
III. Diagnostic Approach to Arrhythmias
A. Bradyarrhythmias
C. Tachyarrhythmias
V. Treatment of Arrhythmias
A. Bradyarrhythmias
B. Tachyarrhythmias
I. Pathophysiology
A. Bradyarrhythmias
1. Pathophysiology: Type Pathophysiology Causes poblockers Sinus Bradycardia VSA Node firing > Electrical signals from Atria to Ventricles - 1 Vagal Tone - Sympathetic Tone - Nodal Blockers - T Vagal Tone AV Node Block AV Node activity or Conduction Block > Electrical signals from Atria to Ventricles - Sympathetic Tone - Nodal Destruction a) SA Node Activity or \ Automaticity o SA node firing -> \ SA node to AV node conduction -> Electrical signals carried from the atria to the ventricles -> Ventricular depolarization -> Ventricular contraction -> Heart Rate (< 50 bpm) SA Node Dysfunction ISA Node to AV Node Conduction 1 IHR ( < 50 ) 260 b) \ AV Node Activity or Conduction Block o AV node conduction -> \ Electrical signals carried from the atria to the ventricles -> \ Ventricular depolarization -> Ventricular contraction -> \ Heart Rate (< 50 bpm) AV Node Dysfunction - JAV Node Conduction 1 IHR ( < 50 )
ARRHYTHMIAS CARDIOLOGY : NOTE #2 NINJA NERD 0 1 of 22 00:20
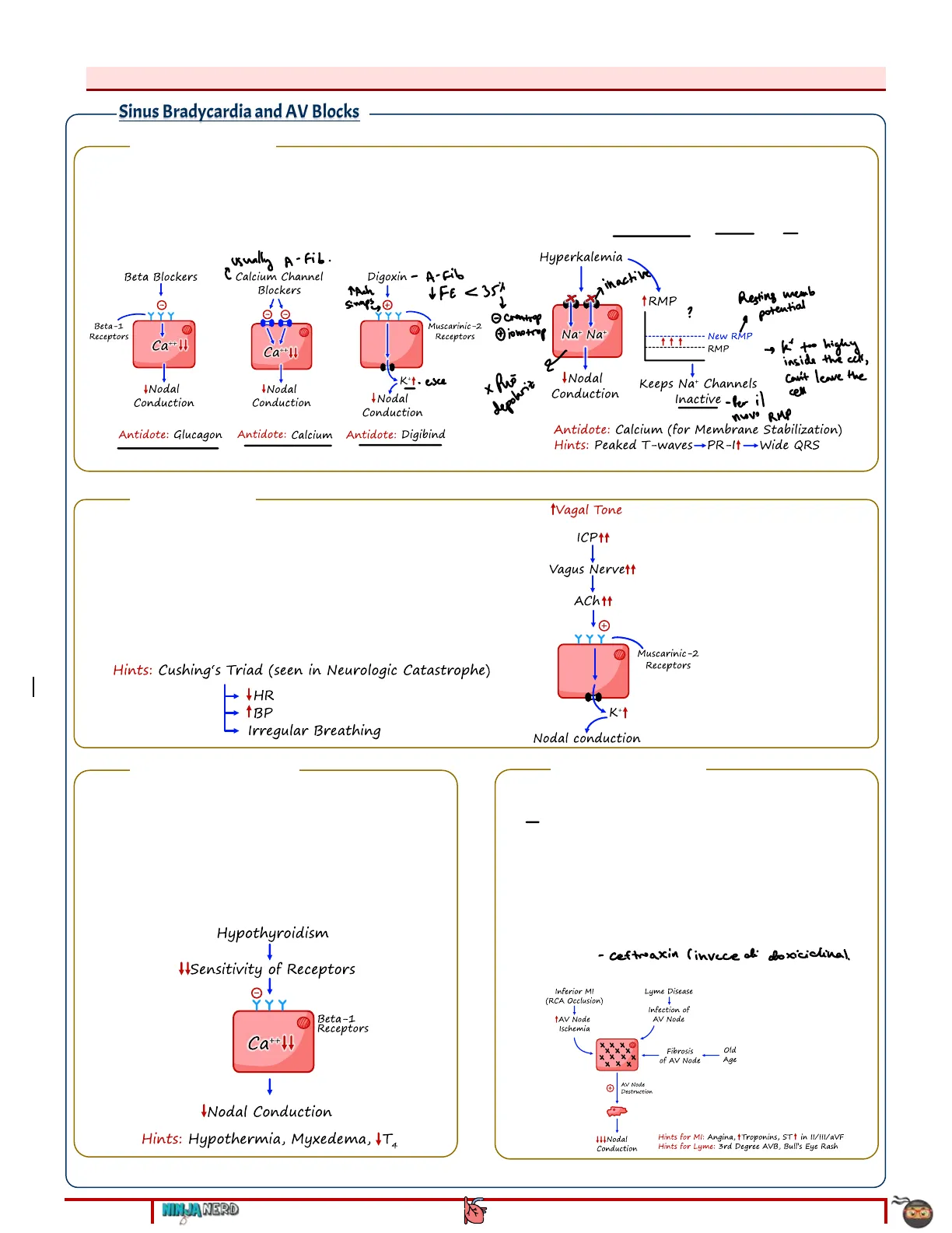
- Nodal Blockers -Causes of Bradyarrhythmias: Sinus Bradycardia and AV Blocks i) Nodal Blockers o Beta-Blockers, Calcium Channel Blockers, Digoxin -> Suppress the SA node and the AV node -> leading to electrical conduction from the atria to the ventricles Assess medication history for these medications that are often used in atrial fibrillation or hypertension usually A- Fib. Beta Blockers 1 YYY Beta-1 Receptors 1 Ca++14 Ca++11 INodal Conduction + Nodal Conduction I Nodal Conduction Antidote: Digibind o Hyperkalemia -> Suppresses the AV node conduction -> Results in Electrical conduction from the atria to the ventricles Assess for peaked T-waves, wide QRS on ECG Hyperkalemia athactive TRUMP ? . Na+ Na+ New RMP RMP 2 1 I Nodal Conduction Keeps Na+ Channels Inactive- Per il nuovo RMP Antidote: Calcium (for Membrane Stabilization) Hints: Peaked T-waves-PR-It-Wide QRS ii) 1 Vagal Tone o TICP -> 1Vagus Nerve stimulation -> suppresses the AV node -> leading to electrical conduction from the atria to the ventricles Assess for Cushing's Triad: · Bradycardia · Hypertension . Irregular breathing pattern Hints: Cushing's Triad (seen in Neurologic Catastrophe) IHR Irregular Breathing 1Vagal Tone ICP11 1 Vagus Nervett Acht1 1 YYY Muscarinic-2 Receptors K + 1 Nodal conduction -iii) \Sympathetic Tone o Hypothyroidism -> \Sensitivity of the Beta-1-receptors and BMR of AV node -> Suppresses the AV node -> Results in Electrical conduction from the atria to the ventricles Assess for features of hypothyroidism and especially hypothermia seen in myxedema coma Hypothyroidism WSensitivity of Receptors 1 Y Y Beta-1 Receptors Ca++11 1 INodal Conduction Hints: Hypothermia, Myxedema, IT4 -iv) Nodal Destruction o Inferior Myocardial infarction (RCA occlusion) -> AV node infarction -> leading to Velectrical conduction from the atria to the ventricles Assess for chest pain, 1 Troponins, And ST1 in II/III/aVF o Old age -> AV node fibrosis/scars -> Results in Electrical conduction from the atria to the ventricles o Lyme Disease -> Borrelia burgdorferi infection -> AV node destruction - ceftwaxin (invece di doxiciclina). Assess for Bull's Eye Rash, 3rd Degree AV block Lyme Disease Inferior MI (RCA Occlusion) 1 tAV Node Ischemia Infection of AV Node Old Fibrosis of AV Node - Age AV Node Destruction 444 Nodal Conduction Hints for MI: Angina, tTroponins, STt in II/III/aVF Hints for Lyme: 3rd Degree AVB, Bull's Eye Rash
2 of 22 NINJA NERD CARDIOLOGY: NOTE #2 ARRHYTHMIAS TAch 1 simps Y Muscarinic-2 Receptors K+ . esce + depolariz , k' too highy inside the cell, can't leave the cell Antidote: Glucagon Antidote: Calcium C Calcium Channel Blockers Digoxin - A-Fib IFE<35% Resting memb potential 2 O crontrop 2 jonotrop
B. Tachyarrhythmias
08:44 1. Pathophysiology i) 1 Automaticity o 1 SA Node firing -> ^ SA Node to AV node conduction -> 1Electrical Signals carried from the atria to the ventricles -> 1 Ventricular Depolarization -> ^ Ventricular Contraction -> 1Heart Rate (> 100 bpm) A normal - SATUL fine Y abnormal - altro focus TV tire It Sympathetic Tone - ISA Node Conduction +Beta-1 Receptors IHR -tAV Node - Conduction INE/EPI YY Beta- 1 Receptors Ca++tt Nodal Conductiontt ii) 1 Re-Entry o Electrical impulses circulating within a loop of cardiac tissue continually stimulate cardiac tissue -> 1 Electrical signals carried from the atria to the ventricles -> ™Ventricular Depolarization -> ^Ventricular Contraction -> o 1 Heart Rate (> 100 bpm) Requires a Premature Stimulus: . 1 Automaticity . 1 Triggered Activity . Types of Anatomical Re-entry: · AVRT · AVNRT IRe-Entry Atrial Re-Entrant Circuits Ventricular Re-Entrant Circuits Atrial Remodelin Ventricular Remodeling 11/2 PILAR ttAtrialtt Stretch 1 ttVentricular Fibrosis/Stretchtt 1 CHF HTN Mitral Stenosis Myocardial CHF (EF< 35%) Infarction -iii) 1 Triggered Activity o Cardiac tissue undergoes after depolarizations before it has a chance to fully repolarize -> Ectopic action potentials are generated -> ^ Electrical signals carried from the atria to the ventricles -> ^Ventricular Depolarization -> ^Ventricular Contraction -> 1Heart Rate (> 100 bpm) . Early After Depolarization (EAD) . Prolonged QT Interval Delayed After Depolarization (DAD) . 1Calcium Influx tTriggered Activity + tAtrial Ectopy 1 HRt IVentricular Ectopy + HRİ Early after Depolarization Delayed after Depolarization ttQT-Interval 1 ttEAD's It Calcium Influx 1 ttDAD's
ARRHYTHMIAS CARDIOLOGY : NOTE #2 NINJA NERD 3 of 22 usualy: - changes in the tissue
2. Causes of Tachyarrhythmias
a) Sinus Tachycardia
1 Automaticity o 1 Sympathetic Tone -> Enhanced automaticity · Fever . Secondary to 1 Basal Metabolic rate Proponolol o Assess for Temp > 38 ℃ or > 100.4 ºF + LT " Hyperthyroidism . Secondary to 1 Basal Metabolic rate and Beta-1 receptor sensitivity o Assess for weight loss, heat intolerance, tremors, diarrhea Beta-1 Agonist . Due to 1 Sympathomimetic Effect o 1 Albuterol Treatments - Asma o 1 Norepinephrine Or Epinephrine o Cocaine or methamphetamine o Pheochromocytoma - palpitations , headack , diaporisis, TP, Iglicemia? Pain, anxiety hints: Shock < 11BP 110,- / Saturaz 11T3+T4 ttTemperature 1 +Baroreceptors Carotid Chemoreceptors y aorta. Activate SNS Activate SNS I Sensitivity of Beta-1 Receptors +Metabolic Rate 1 TINE/ EPITT + + + Beta-1 Receptors YYY + Na+t 1Ca++ 1 Nodal Conduction
b) Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia
-i) 1 Automaticity o 1 Sympathetic Tone -> Enhanced automaticity "Hypoxemia - usually due to this . Seen in COPD 4 of 22 NINJA NERD CARDIOLOGY: NOTE #2 ARRHYTHMIAS · Hypotension . This is a compensatory response to hypotension o Assess for shock (e.g. hypovolemic, septic, obstructive, cardiogenic) · Hypoxemia . This is a compensatory response to hypoxemia o Assess for low sPO2 (e.g. < 90%) or low PaO2 (e.g. < 60 mmHg) Polmonite PNA, COPD, Pulmonary embolism Severe anemia 8 Sympathomimetic Drugs (Act like NE/EPI)
Pathophysiology of Tachyarrhythmias Type Pathophysiology Causes Paroxysmal Supraventricular Tachycardia (PSVT) ₱Re-Entry - Anatomical reentrant pathways Anatomical AVNRT Wolff-Parkinson White (AVRT) Atria AV Node Fibrosis - Bundle of Kent 1 Allows AP's from Atria into Ventricles, thus Bypassing AV Node Slow Pathway Fast Pathway Note: If coupled with AF can generate HR's in 200's Slow Depolarization - Fast Repolarization - Fast Depolarization - Slow Repolarization Hints: Ventricles - PR- 11 Ewide QRS Delta Wave Hint: No P-waves, or Retrograde P-wavesPt ce l'hanno À tutti i meccanismi
c) Atrial Fibrillation and Atrial Flutter
i) 1 Automaticity and Triggered Activity o 1 Sympathetic Tone -> Enhanced automaticity/DADS · Hypotension . This is a compensatory response to hypotension o Assess for shock (e.g. hypovolemic, septic, obstructive, cardiogenic) · Hypoxemia . This is a compensatory response to hypoxemia o Assess for low sPO2 (e.g. < 90%) or low PaO2 (e.g. < 60 mmHg) · PNA, COPD, Pulmonary embolism Severe anemia . Hyperthyroidism . Secondary to 1 Basal Metabolic rate o Assess for weight loss, heat intolerance, tremors, diarrhea · Beta-1 agonist . Due to 1 Sympathomimetic effect o 1 Albuterol Treatments o 1 Norepinephrine Or Epinephrine o Cocaine or methamphetamine o Pheochromocytoma o Electrolyte Abnormalities -> Enhances triggered activity (TEADs) · Hypokalemia or Hypomagnesemia . Assess for T-wave inversion or U- waves TEAD'S Hypokalemia Hypomagnesemia + QT-Intervaltt Prolong Depolarization + 1 TEAD'S ii) 1 Re-Entry o 1 Atrial Stretch Valvular heart disease (e.g. Mitral stenosis) -> Left atrial enlargement " Hypertension -> Diastolic HF -> 1 Left Atrial pressures -> Left atrial enlargement Atrial Flutter Hint: - Large Re-Entrant Circuit Cavotricuspid Isthmus Atrial Fibrillation Hints: Multiple Re-Entrant Circuits 1 Around Entry of Pulmonary Veins - Usually
ARRHYTHMIAS CARDIOLOGY : NOTE #2 NINJA NERD 0 5 of 22
e) Monomorphic Ventricular Tachycardia or Polymorphic Ventricular Tachycardia (Normal QT Interval)
-i) 1 Automaticity and Triggered Activity o 1 Sympathetic Tone -> Enhanced automaticity and triggered activity · Hypotension . This is a compensatory response to hypotension o Assess for shock (e.g. hypovolemic, septic, obstructive, cardiogenic) · Hypoxemia . This is a compensatory response to hypoxemia o Assess for low sPO2 (e.g. < 90%) or low PaO2 (e.g. < 60mmHg) · PNA, COPD, Pulmonary embolism · Severe anemia Beta-1 Agonist . Due to 1 Sympathomimetic effect o Norepinephrine or Epinephrine o Cocaine or methamphetamine o Pheochromocytoma o Drug Toxicity -> Enhances triggered activity (IDADs) . Digoxin Toxicity o Myocardial Ischemia -> Enhances triggered activity (1 DADs) Assess for angina, 1 Troponins, and ST changes o Electrolyte Abnormalities -> Enhances triggered activity (1 EADS) · Hypokalemia Or Hypomagnesemia . Assess for T-wave inversion or U- waves tTriggered Activity TEAD'S tDAD'S 1 Simpatico M Ca+ Probugets QT. Hypokalemia Hypomagnesemia Own Cause triggered activity + rientry Myocardial Infarction t Sympathetic Tone Digoxin Toxicity Angina Troponint ST Changes - Improves with Antidote (Digibind) NA+/K+ ATPase QT-Intervaltt 1 Loss of Cell Integrity Beta-1 Receptor IIntracellular Na Can't Exchange tCa" Influx up. I TEAD's İDAD's ii) Re-Entry o Ventricular Scars/Fibrosis Myocardial infarction - the most common cause Heart Failure with Reduced EF (HFrEF < 35%) Ventricular Tachycardia Hints: Re-Entrant Circuit One - Monomorphic 2 or more -Polymorphic 1 1 foci
6 of 22 NINJA NERD CARDIOLOGY: NOTE #2 ARRHYTHMIAS Prolong Depolarization Calcium - ca+ Luileds