Risk Management in the Financial System: Functions and Techniques
Document about Risk Management. The Pdf introduces the fundamental concepts of risk management within the financial system, including its components, functions, and various techniques. This University level material for Economics students, authored by an expert, also delves into incentive problems like moral hazard and adverse selection, providing a comprehensive overview of the subject.
See more18 Pages

Unlock the full PDF for free
Sign up to get full access to the document and start transforming it with AI.
Preview
Introduction to the Financial System
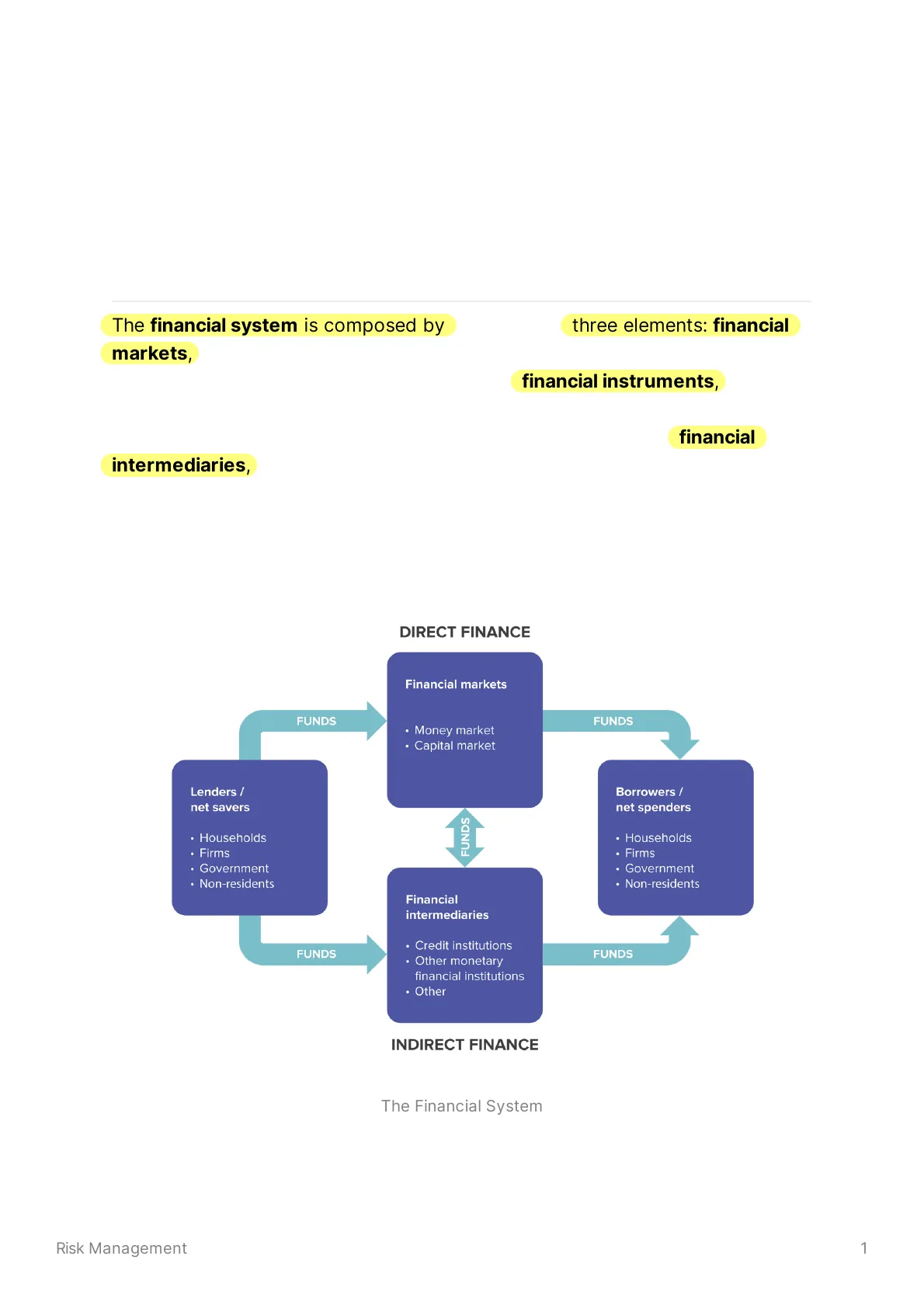
The financial system is composed by the following three elements: financial markets, which are virtual places, such as equity markets and derivatives markets, where the flow of funds takes place; financial instruments, which are the tools, such as shares, bonds, derivatives, that allow the flow of funds and are usually represented by a contract that involves two parties; financial intermediaries, which are primarily banks, insurances and pension funds. The primary function of the financial system is to transfer funds from lenders and savers to borrowers and spenders. The relationship between the two categories is illustrated below.
Direct and Indirect Finance
DIRECT FINANCE Financial markets FUNDS FUNDS · Money market · Capital market Lenders / net savers Borrowers / net spenders · Households FUNDS · Households · Firms · Firms · Government · Government · Non-residents · Non-residents Financial intermediaries · Credit institutions FUNDS FUNDS · Other monetary financial institutions · Other INDIRECT FINANCE The Financial System
1If the transfer of funds takes place through the financial market alone, regardless of the type of market, and without the intervention of financial intermediaries, that transaction falls into the classification of direct finance. On the other hand, if the exchange of funds is managed by a financial intermediary, this operation is classified as indirect finance.
The presence of financial markets does not imply that financial intermediaries are useless in the activity of fund transfering. Intermediaries are linked to financial markets, because fund transfer through them represents the biggest part of the activity of all financial institutions. Outside of the picture above we can find the central bank, which puts money inside the system or takes it back for a lot of purposes, such as monetary policies.
Functions of the Financial System
The full list of functions served by the financial system contains the following five.
- Transfering of resources across time and space.
- Clearing and settlement of payments.
- Transmission of monetary policies. Central banks transmit their decisions in regards to policies by varying prices and interest rates, interacting with the financial system.
- Providing information on prices. Price information is needed to perform any sort of financial operation.
- Managing risks.
Risk Transfer in the Financial System
Given that the one of the main functions of the financial system is to transfer risks, the financial system itself can also be seen as a flow of risk and not just funds. In general, when funds are transferred, the risks linked to each type of fund is transferred as well. The transfer of risk can be either bundled or unbundled.
- Bundled means that the transfer of risk is incorporated with the flow of funds. An example of bundled risk transfer could be depositing money into a bank: if I deposit some money in a bank, my deposit is subjected to many risks, such as the risk of the bank going bankrupt. This is the reason why we employ deposit protection schemes, so that we can protect depositors from these risks.
- Unbundled means that the transfer of risk is separated from the flow of funds. For example: when I negotiate a future contract with reference to an Risk Management 2underlying asset, I am unbundling the risk, separating it from the transfer of funds. This is the reason why derivatives were invented: allowing unbundled risk transfers.
Risk Management Techniques
Risks influence the economic decisions of several categories of market participants: households, firms, governments and financial intermediaries. Financial intermediaries are the most complicated ones, because they both have their own risk management activities and provide these services to other economic actors: in simpler terms, they have to manage both their risks and the ones of other people.
Risk management techniques can be divided into the following three categories.
- Risk bearing: I accept the risks that I have and I manage them internally.
3
- Risk pooling: multiple risks are put together and managed using a portfolio-like approach in order to diversify the exposure to the individual risks. This is, for example, the core business of insurances.
- Risk transfer: factors of risk are removed from the firm and transfered elsewhere. Risk transfering is not possible every time, but only when the proper instrument to do so is accessible.
Managing risks does not mean choosing one of the three types mentioned above. Most of the times, firms adopt a mixed approach that involves two or more of these techniques. For instance: in the securitization of loans, banks have to bear the riskiest part of the operation, while the other part can be transfered; this represents a mix of risk bearing and risk transfer.
There is a trade off between the benefit of eliminating the risk and the cost of removing that risk. The process of evaluating this trade off by performing a benefit-cost analysis in order to decide on the best course of action to take, is called risk management.
Hedgers vs. Speculators
If we face a particular type of risk, it means we have a particular risk exposure. This implies that risks can only be assessed with reference to something, and they cannot be evaluated in isolation or in an idealistic way. The presence of a risk exposure allows us to distinguish between a hedger and a speculator.
- Hedgers interact with the market in order to protect their investment portfolios when they are exposed to risks. In other words, their operations Risk Management 3are linked to what they have in their portfolio, and their goal is to balance their total risk.
- Speculators are people who perform operations that are not linked with their risk exposure. Speculators are not interested primarily in protecting their investment, but are looking to produce a profit out of their activities.
Activities for Risk Transfer
The financial system plays a major role in the activity of risk transfering, as it allows firms to perform a wide array of activities listed below.
- Selling the risk to another firm.
- Hedging the risk to balance their portfolio.
- Insure the risk against adverse scenarios.
- Diversify the risk, by balancing out risky operations with more stable ones.
- Designing financial contracts and securities, which can be used to transfer risk.
Limitations in Risk Allocation
There are factors that limit the efficient allocation of risks into the financial system: these are transaction costs and incentive problems. When we talk about incentive problems, we are referring to two main scenarios:
- Moral hazard is the risk that a party has not entered into a contract in good faith or has provided misleading information about its assets, liabilities, or credit capacity. In addition, moral hazard also may mean a party has an incentive to take unusual risks in a desperate attempt to earn a profit before the contract settles. Moral hazards can be present at any time two parties come into agreement with one another. Each party in a contract may have the opportunity to gain from acting contrary to the principles laid out by the agreement.
- Adverse selection refers generally to a situation in which sellers have information that buyers do not have, or vice versa, about some aspect of product quality. In other words, it is a case where asymmetric information is exploited. Asymmetric information, also called information failure, happens when one party to a transaction has greater material knowledge than the other party. Typically, the more knowledgeable party is the seller. Symmetric information is when both parties have equal knowledge.
Banking Overview
Moving on to the main subject of this course, let's do a quick recap on banking. When we talk about banking, we need to make some assumptions first.
Assumptions About Banks
Risk Management 4ASSUMPTIONS ABOUT BANKS
- There is no perfect competition in the market of deposits and credits, which are the markets banks are most involved in. Large banks are usually in a dominant position from which they can greatly influence prices at the expense of smaller banks.
- Information is not distributed in a symmetrical way. For example, let's think about your average depositor in a bank: he does not know whether the bank he is depositing money into is a good bank or not, whereas the bank does a lot of research on the depositor and knows his situation very well.
- Economies of scale and scope play a major role. Economies of scales are strictly related to the size of the bank, and they allow larger banks to provide more services to customers when compared to smaller banks.
- Transaction costs are an everpresent factor that makes the market less efficient.
- Uncertainty is typical of any financial negotiation. It can be mitigated, but not removed entirely.
Nature of a Bank
The nature of a bank can be analyzed from several points of view. First of all, a bank is a financial intermediary because it performs the transfering of funds and risks. The bank is also a firm, meaning that it has to create value for its shareholders. This will be different depending on location: from an Anglosaxon perspective, shareholder value creation is the most important thing; from an European perspective, stakeholder value is more important. Finally, a bank is a regulated organization: due to their importance in the financial stability of a country, banks are highly regulated.
Bank Balance Sheet
ASSET LIABILITY Deficit Units Equity Surplus Units The balance sheet of a bank is divided into two parts: assets and liabilities, as illustrated in the picture above. Banks take money from surplus units and invest money in deficit units.
The asset side of a bank balance sheet is composed of investments, loans, real assets and financial assets. This is where banks invest their money and from where they take interests and dividends. The liability side is mainly Risk Management 5comprised of deposits, from which the bank obtains the money it uses to invest. Equity is the capital owned by the shareholders of the bank: we can find it in the liability side, but it is not considered a liability.
On-Balance Sheet vs. Off-Balance Sheet Items
With regards to the bank balance sheet, we can distinguish on-balance sheet items from off-balance sheet ones.
On balance sheet items are the ones written in the balance sheet.
- Off balance sheet items refer to assets or liabilities that do not appear on the bank's balance sheet, but are nonetheless effectively in the possession of the bank. Assets or liabilities designated off balance sheet are typically ones that the bank is not the recognized legal owner of, or in the case of a liability, does not have direct legal responsibility for. As an example. when some loans are securitized and sold off as investments, the securitized debt will be kept off the bank's books.
Functions of Banks
Banks have three main functions.
- Investment function, as banks allocate their capital in the markets.
- Credit function, which is a peculiar type of investment function. Loans are credits that banks have toward their borrowers. For a bank to give credit to a borrower, the bank evaluates if the creditor will be able to pay back and monitors the relationship once he has received the credit. From the bank's perspective, this is equal to investing a sum of money and earning interest at the end of the loan.
- Transformation function, because banks collect money with different maturities, varied amounts, different currencies, different contracts and different risks; they transform assets in liabilities, as well as collecting money with a specific set of characteristics and giving it back with different characteristics.
Bank Structure: Business Poles, Lines, and Activities
Banks can be divided into business poles, business lines and activities.
- Business poles are the various parts the activity of the bank is divided in: retail banking, investment banking, trading, private banking and so on.
- Business lines represent the groups of activities inside each of the bank's business pole.
- Activities are the individual activities each business line is composed by, and they can overlap between different business lines. Risk Management 6