Circulatory System and Cardiac Cycle: Understanding Heart Function
Slides about the Circulatory System, Cardiac Cycle. The Pdf provides a detailed explanation of the cardiac cycle and circulatory system, including the "lub-dup" sounds and intrinsic control of the heartbeat. This Biology resource is suitable for University students.
See more15 Pages

Unlock the full PDF for free
Sign up to get full access to the document and start transforming it with AI.
Preview
Cardiac Cycle Overview
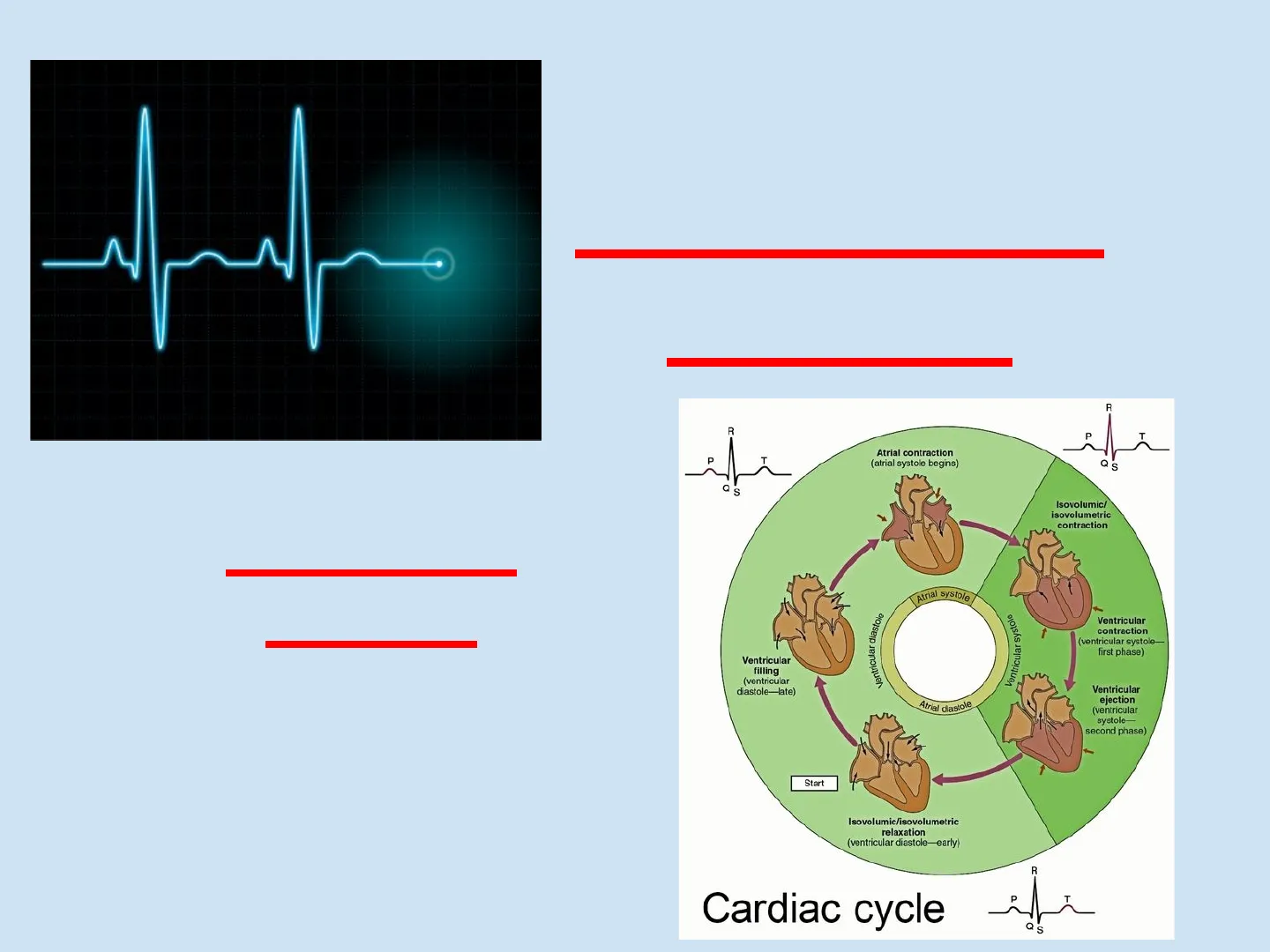
Cardiac Cycle Circulatory System R R P T P T Atrial contraction (atrial systole begins) Q S Q S Isovolumic/ isovolumetric contraction Atrial systole Ventricular diastole Ventricular systole Ventricular contraction (ventricular systole- first phase) Ventricular filling (ventricular diastole-late) Atrial diastole Ventricular ejection (ventricular systole- second phase) Start Isovolumic/isovolumetric relaxation (ventricular diastole-early) R Cardiac cycle P T Q SCardiac Cycle Each heartbeat is called a cardiac cycle. The heart is a "double pump" since both sides of the heart contract simultaneously, but the right side pumps blood to the lungs while the left side pumps blood to the body.
Systole: contraction of the heart muscle. Diastole: relaxation of the heart muscle. One heartbeat lasts about 0.85 second.
Phases of the Cardiac Cycle
2Cardiac Cycle Atria contract pushing blood into the ventricles Semilunar valves closed 2 Atrial systole; ventricular diastole 0.1 sec Semilunar valves open AV valves open 0.4 sec 0.3 sec All 4 chambers rest and refill. 1 Atrial and ventricular diastole AV valves closed Ventricles contract, pushing blood to the pulmonary arteries and aorta. 3 Ventricular systole; atrial diastole
Heart Sounds
3The "lub-dup" sounds associated with heartbeat are from the closing of the valves after contractions.
- Lub: atrioventricular valves close
- Dup: semilunar valves close
Heart Chambers and Blood Flow
4Sinoatrial node Atrioventricular node (a) Cardiac diastole: all chambers are relaxed, and blood flows into the heart. (b) Atrial systole, ventricular diastole: atria contract, pushing blood into the ventricles. 1 (c) Atrial diastole, ventricular systole: after the atria relax, the ventricles contract, pushing blood out of the heart.
Intrinsic Control of Heartbeat
5Intrinsic Control of the Heartbeat 6. Intrinsic control means that the heart instigates the heartbeat all by itself.
- The right atrium of the heart has nodal tissue.
- The Sinoatrial Node (SA node) is located in the upper dorsal wall of the right atrium.
- The Atrioventricular Node (AV node) is located in the base of the right atrium near the septum.
Sinus Node Atrium AV Node Ventricles
Mechanism of Intrinsic Control
7How does Intrinsic Control work?
- The SA node initiates heartbeat every 0.85 s so it is known as the pacemaker of the heart.
- The SA node signals the atria to contract.
- The nerve impulse from the SA node moves to the AV node and then through the two branches of the atrioventricular bundle and along smaller Purkinje fibers, which branch throughout the myocardium.
- These signals cause the ventricles to contract.
Cardiac Cycle Animation
8Cardiac Cycle AnimationElectrocardiogram (ECG) An ECG is a recording of a person's heartbeat. Electrical changes in the myocardium can be detected on the skin. It consists of three sections:
- P wave
- QRS wave
- T wave
R wave T wave P wave ST segment Q wave | S wave
ECG Wave Interpretation
10
- The P wave indicates that the atria are contracting to pump out blood.
- The QRS wave indicates that the ventricles are contracting to pump out blood.
- The next upward curve is called the T wave. The T wave indicates that the ventricles are resting.
R wave T wave P wave ST segment Q wave | S wave
Extrinsic Control of Heartbeat
11Extrinsic Control of the Heartbeat
Nervous Control of Heartbeat
12Nervous control The medulla oblongata (part of the brain) controls heartbeat with the Autonomic Nervous System (unconscious control).
- The Parasympathetic Nervous System acts to slow down the heartbeat by decreasing nodal activity.
- The Sympathetic Nervous System speeds up the heartbeat by increasing nodal activity.
Hormonal Control of Heartbeat
13Hormonal control
- The Adrenal Medulla is the inner part of the Adrenal Gland found on top of each kidney.
- The adrenal medulla releases the hormones Epinephrine (Adrenalin) and Norepinephrine (Noradrenalin).
- Both of these hormones stimulate the heart to pump stronger and faster.
Medulla Cortex Right adrenal gland Left adrenal gland Kidney Kidney
Nervous and Hormonal Control Synergy
14Why have both nervous AND hormonal control of the heartbeat?
15