Detailed tables on human muscles anatomy
Outlines from University about detailed tables on human muscles anatomy. The Summaries provide a concise reference for studying muscular anatomy, covering facial, mastication, neck, back, and lower limb muscles. This Biology document is ideal for university students.
See more17 Pages
Unlock the full PDF for free
Sign up to get full access to the document and start transforming it with AI.
Preview
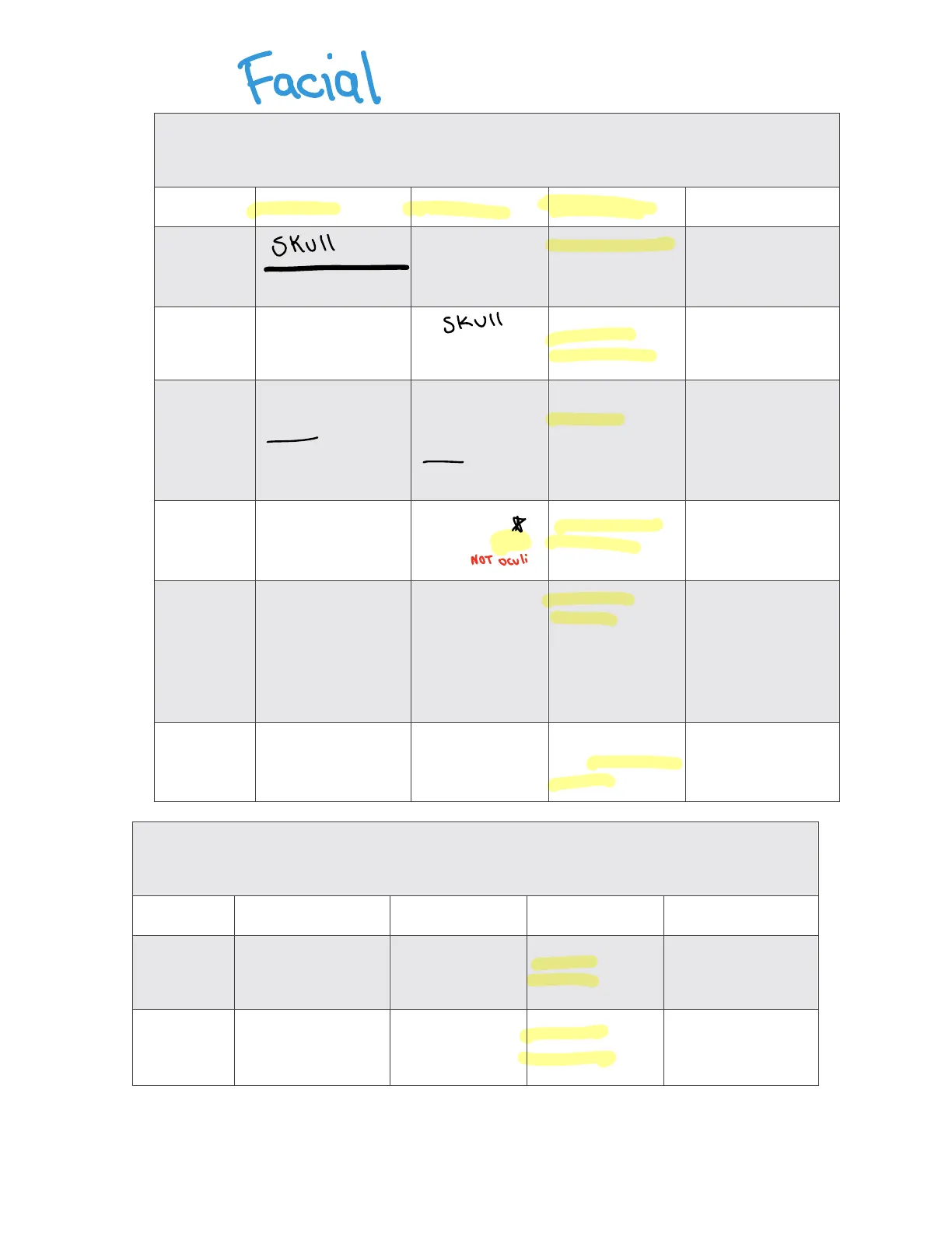
Facial Muscles
Muscles of Facial Expression
All are innervated by the facial nerve (CN VII)
Muscle Origin Insertion Action Innervation
Skull
Frontalis Cales aponeurotica Skin of eyebrows and root of nose Raises eyebrows; wrinkles forehead Facial nerve (CN VII)
Occipitalis Occipital and temporal bone Skull Galea aponeurotica Pulls scalp posteriorly Facial nerve (CN VII)
Orbicularis oculi Frontal and maxillary bones Tissue of the eyelid Produces blinking, squinting, and draws eyebrows inferiorly Facial nerve (CN VII)
Buccinator Maxilla and mandible Orbicularis oris NOT Oculi Compresses the cheek (as in whistling) Facial nerve (CN VII)
Orbicularis oris Arises indirectly from the maxilla and mandible Encircles the mouth, inserts onto skin and muscles at lateral corners of mouth Closes the lips; purses and protrudes the lips, as in whistling and kissing Facial nerve (CN VII)
Mentalis Mandible Skin of the chin Protrudes lower lip; wrinkles the chin Facial nerve (CN VII)
Muscles of Mastication (Chewing)
All are innervated by the trigeminal nerve (CN V)
Muscle Origin Insertion Action Innervation
Masseter Zygomatic arch Mandible Elevates mandible Trigeminal nerve (CNV)
Temporalis Occipital and temporal bone Mandible Elevates mandible Trigeminal nerve (CNV)
Muscles of the Neck and Back
All are innervated by spinal nerves except sternocleidomastoid
Muscle Origin Insertion Action Innervation
Splenius Vertebrae Cz-T6 Temporal and occipital bone Acting together extend the head; acting alone head is rotated and bent toward the same side Spinal nerves
Sternocleidomastoid Sternum and clavicle Mastoid process of the temporal bone Acting together flex the head; acting alone rotates head toward the opposite shoulder Accessory nerve (CN XI)
Semispinalis Vertebrae C7-T12 Occipital bone and cervical and thoracic vertebrae (to T4) Extends vertebral column and head, rotates to opposite side Spinal nerves
Erector spinae group - prime movers of back extension, arranged as three vertically running columns from medial to lateral:
Spinalis (most medial) Upper lumbar to lower thoracic vertebrae Upper thoracic to cervical vertebrae Extends vertebral column Spinal nerves
Longissimus (intermediate) Lumbar through cervical vertebrae Thoracic through cervical vertebrae and rib Extend and laterally flex vertebral column
Muscles of the Thorax
Muscles of the Thorax Relating to Respiratory Movements
All are innervated by intercostal nerves except the respiratory diaphragm
Muscle Origin Insertion Action Innervation
External intercostals Inferior border of the rib above Superior boarder of the rib below Elevates rib cage, assists in forced inspiration Intercostal nerves
Internal intercostals Superior border of the rib below Inferior border of the rib above Depress the rib cage, assists in forced expiration
Respiratory diaphragm Rib cage, sternum, and lumbar vertebrae Central tendon Prime mover of inspiration Phrenic nerve
Muscles of the Thorax Relating to Movements of the Scapula
Muscle Origin Insertion Action Innervation
Pectoralis minor Ribs 3-5 Scapula Stabilizes scapula by drawing it forward and downward Pectoral nerves
Serratus anterior Ribs 1-8 Scapula Protracts and holds scapula against the thoracic wall Long thoracic nerve
Trapezius Superior nuchal line, ligamentum nuchae, and vertebrae C7 through T12 Clavicle, scapula Elevates, retracts, and rotates scapula Accessory nerve (CN XI)
Levator scapulae Vertebrae C1 through C4 Scapula Elevates the scapula Cervical spinal nerves and dorsal scapular nerve
Rhomboids Vertebrae C7 through T5 Scapula Retracts and stabilizes scapula Dorsal scapular nerve
Muscles Acting on the Arm
Anterior Group
Muscle Origin Insertion Action Innervation
Pectoralis major Sternum, costal cartilages, and clavicle Humerus Flexes, adducts, and medially rotates arm Pectoral nerves
Deltoid (anterior fibers) Clavicle (scapula for lateral and posterior fibers) Deltoid tuberosity of the humerus Flexes, extends, abducts, and medially rotates arm Axillary nerve
Coracobrachialis Scapula Humerus Flexes and adducts arm Musculocutaneous
Biceps brachii Long head Short head Scapula Radius Weak shoulder flexion (also flexes the elbow and supinates forearm) Musculocutaneous
Posterior Group
Muscle Origin Insertion Action Innervation
Deltoid (lateral and posterior part) Scapula Humerus Flexes, extends, abducts, and laterally rotates arm Axillary nerve
Supraspinatus* Scapula Greater tubercle of the humerus Assists in arm abduction, stabilizes shoulder joint Suprascapular nerve
Infraspinatus* Scapula Greater tubercle of the humerus Laterally rotates arm, stabilizes shoulder joint Suprascapular nerve
Teres minor* Scapula Greater tubercle of the humerus Laterally rotates arm, stabilizes shoulder joint Axillary nerve
Subscapularis* Scapula Lesser tubercle of the humerus Medially rotates arm, stabilizes shoulder joint Subscapular nerve
Teres major Scapula Humerus Extends, adducts, and medially rotates arm Subscapular nerve
Triceps brachii long head Scapula Ulna Extends and assists in arm adduction Radial nerve
Latissimuss Dorsi Thoracic and lumbar vertebrae, ribs, iliac crest Humerus Extends, adducts and medially rotates arm Thoracodorsal nerve
*SITS = muscles of the rotator cuff, major stabilizer of the shoulder joint
Muscles Acting on the Forearm
Anterior Flexor Compartment
Muscle Origin Insertion Action Innervation
Biceps brachii Scapula Radius Flex and supinate forearm Muculocutaneous nerve
Bracialis Humerus Ulna Flex forearm
Pronator Teres Humerus and proximal ulna Radius Pronates forearm Median nerve
Brachioradialis Humerus Radius Flexes forearm Radial nerve
Posterior Extensor Compartment
All are innervated by the radial nerve
Muscle Origin Insertion Action Innervation
Triceps brachii Long head Scapula Lateral head Humerus Ulna Extends forearm at elbow Radial nerve
Medial head Humerus
Supinator Humerus and ulna Radius Supinates forearm
Muscles Acting on the Wrist and Hand
Anterior Flexor Compartment
Muscle Origin Insertion Action Innervation
Palmaris longus Medial epicondyle of the humerus Palmar aponeurosis Flex wrist Median nerve
Flexor carpi ulnaris Medial epicondyle of the humerus and ulna Fifth metacarpal and pisiform and hammate Flex wrist, adducts hand Ulnar nerve
Flexor carpi radialis Medial epicondyle of the humerus Second and third metacarpal Flex wrist, abducts hand Median nerve
Flexor digitorum superficialis Medial epicondyle of the humerus, ulna, and radius Phalanges of fingers 2-5 Flexes wrist and middle phlanges of fingers 2-5 Median nerve
Flexor digitorum profundus Ulna Phalanges of fingers 2-5 Flexes distal and proximal interphalangeqal joint, metacarpophalangeal joint, and wrist Median (lateral half) and ulnar (medial half) nerves
Flexor pollicis longus Radius Thumb Flexes distal phalanx of the thumb Median nerve
Posterior Extensor Compartment
All are innervated by the radial nerve
Muscle Origin Insertion Action Innervation
Extensor carpi radialis longus Second metacarpal Extends and abducts wrist
Extensor carpi radialis brevis Third metacarpal Extends and abducts wrist Lateral epicondyle of the humerus Radial nerve
Extensor carpi ulnaris Fifth metacarpal Extends and adducts wrist
Extensor digitorum Phalanges of fingers 2-5 Prime mover of finger extension, extends wrist
Muscles of the Anterior and Lateral Abdominal Wall
- All are innervated by intercostal nerves
Muscle Origin Insertion Action Innervation
External abdominal oblique Lower 8 ribs Linea alba Rotates vertebral column and compresses abdominal contents
Internal abdominal oblique Iliac crest Linea alba Rotates vertebral column and compresses abdominal contents Intercostal nerves
Rectus abdominus Pubis Xiphoid process and ribs Flexes vertebral column and compresses abdominal contents
Transversus abdominus Last 6 ribs and iliac crest Linea alba Compresses abdominal contents
Hip Flexors
Anterior Compartment Hip Flexors
All are innervated by the femoral nerve
Muscle Origin Insertion Action Innervation
Iliacus Ilium Femur Flexes thigh
Psoas Lumbar vertebrae Femur Flexes thigh
Rectus femoris Ilium Tibia Flexes thigh (and extends knee) Femoral nerve
Sartorius Ilium Tibia Flexes, abducts, and laterally rotates the thigh ("tailor's muscle")
Pectineus Pubis Femur Flexes, adducts and medially rotates thigh
Hip Extensors
Posterior Compartment Hip Extensors
- All are innervated by the sciatic nerve (except for gluteus maximus)
- Have an origin on the ischial tuberosity (except for the gluteus maximus)
Semimembranosus, semitendinosus, and biceps femoris are collectively known as the hamstrings
Muscle Origin Insertion Action Innervation
Gluteus maximus Ilium and sacrum Gluteal tuberosity of the femur Extends, abducts and laterally rotates thigh Inferior gluteal nerve
Semitendinosus Tibia
Semimembranosus Ischial tuberosity Tibia Extends thigh; flexes knee Sciatic nerve
Biceps femoris Fibula8
Hip Adductors
Medial Compartment Hip Adductors
- All are innervated by the obturator nerve (except for the pectinius)
- Have an origin on the ishium and/or pubis
- Insert onto the medial aspect of the femur (except for the gracilis)
Muscle Origin Insertion Action Innervation
Adductor magnus Ischiopubic ramus Femur Adducts, flexes, and medially rotates thigh
Adductor longus Pubis Femur Adducts, flexes, and medially rotates thigh Obturator nerve
Adductor brevis Pubis Femur Adducts, flexes, and medially rotates thigh
Pectineus Pubis Femur Adducts, flexes, and medially rotates thigh Femoral nerve
Gracilis Ischiopubic ramus Tibia Adducts, flexes, and medially rotates thigh; flexes knee Obturator nerve
Hip Abductors
Lateral Compartment Hip Abductors
- All are innervated by the superior gluteal nerve
- Have an origin on the ilium
- Insert onto the greater trochanter of the femur (except for the tensor fasciae latae)
Muscle Origin Insertion Action Innervation
Gluteus medius Femur Abducts and aids in medial rotation of the thigh
Gluteus minimus Ilium Superior gluteal nerve
Tensor fasciae latae Iliotibial tract Abducts, flexes, and aids in medial rotation of the thigh
Extensors of the Knee
Anterior Compartment Extensors of the Knee
- All are innervated by the femoral nerve
- Insert onto the tibial tuberosity
- All four muscles are collectively known as the the quadriceps femoris
Muscle Origin Insertion Action Innervation
Rectus femoris* Ilium
Vastus lateralis Tibial tuberosity Extends knee (rectus femoris also flexes thigh) Femoral nerve
Vastus intermedius Proximal femur
Vastus medialis Femur