Business Process Modeling and Analysis: Data Flow and Object Lifecycle
Slides about Business Process Modeling and Analysis. The Pdf explores data flow, execution semantics, and structured data in subprocesses, focusing on object lifecycle conformance. The Pdf, suitable for University Computer Science students, includes diagrams to illustrate concepts.
See more22 Pages
Unlock the full PDF for free
Sign up to get full access to the document and start transforming it with AI.
Preview
Business Process Modeling and Analysis
Data in Business Processes
3/16/2016 Business Process Modeling and Analysis Data in Business Processes
- Data and Data Flow
- Data Execution Semantics
- Structured Data and Sub-Processes
- Object Lifecycle Conformance
13/16/2016
Data and Data Flow
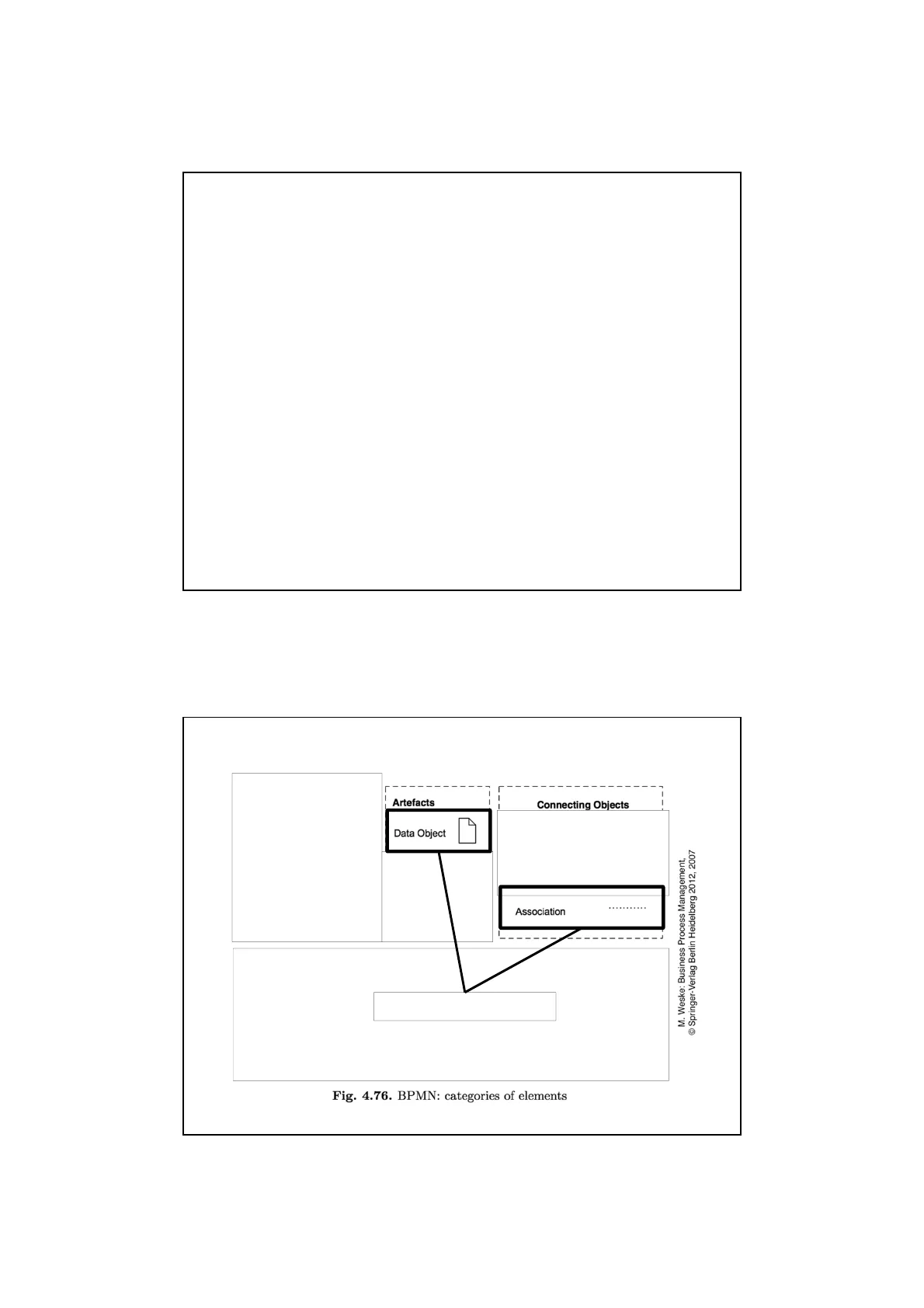
Notation Categories and their Elements
Artefacts Connecting Objects
1 Data Object Association Discussed this week M. Weske: Business Process Management, @ Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg 2012, 2007 Fig. 4.76. BPMN: categories of elements 23/16/2016
Motivation for Data in Processes
. Traditionally, the focus of business process modeling is on activities and control flow Reseller Reject order Order rejected Reseller Check order X Order received Approve order Prepare parcel Send parcel Parcel sent · However - In process models, data objects appear implicitly as labels of activities and events
Motivation for Data in Processes
· Execution of business processes - Data is created, manipulated and used during the execution of a business process - Data serves as input, is created as output, and drives decisions - Representing data objects in process models helps bridging the gap between business and IT, during process implementation · What will be covered - Modeling of data objects - Dependencies between data objects - Possible states of a data object during process execution - Relationships between data and process activities 33/16/2016
Modeling of Data in BPMN
· Notational elements for representing data · Data objects - „items, physical, or information items“ - Data objects with state - Data objects with external structure: lists Order Order [created] Order = · Data storage ERP system · Data from external source for the entire process - Data input Order Order Data Input / Data Output · Data Input / Data Output represent input / output data to the entire process (or sub-process) · If applied to a business process - Data object existed before the start of the process - Data object exists after the termination of the process · Can also be applied to sub-processes 1 DataInput DataOutput 4 - Data output Task3/16/2016
Representing Data Objects
. Dashed edges indicate the reading and writing of data objects by activities Check order Approve order Prepare parcel Send parcel O Parcel sent Order Parcel · Notice - The term „data object“ might be misleading - We represent the type level, not the level of individual data objects
Representing Data Objects Flow
· Data flow between activities related by sequence flow can be expressed in a condensed form Check order Approve order Prepare parcel Send parcel Parcel sent V Order Parcel 53/16/2016
Representing Data Objects Structure
· The structure of data objects is not represented in BPMN - The structure of data objects can be modeled, e.g., in UML class diagrams or entity-relationship diagrams Check order Approve order Prepare parcel Send parcel Parcel sent Order Parcel Concurrent Access A . 1 C 0-0 D - 7 B · Notice - BPMN does not provide means to express transactional properties - Managing concurrent access to data needs to be done by IT systems, e.g., database systems 63/16/2016
Representing Data Object States
· Data objects can have a state, i.e., a representation of its current value - State transitions are triggered by activities, writing data objects Check order Approve order Prepare parcel Send parcel parcel sent Order [checked] Order [approved] Parcel [prepared] Parcel [sent] Check order Approve order Prepare parcel Send parcel parcel sent Order [checked] Order [approved] Parcel [prepared] Parcel [sent]
Example: Data Objects
· The order fulfillment process acts on several data objects Reseller Reject order Order rejected Check order X Order received Approve order Prepare parcel Send parcel Parcel sent Reseller V Parcel [prepared] Parcel [sent] Customer data [verified] Transport document [created] Delivery note [created] 73/16/2016
Data Execution Semantics
Execution Semantics
. So far, only sequence flow decides if and when an activity can be enabled · Data influences execution semantics of processes as well - An activity is enabled only if the data that the activity reads is available and in the required state Check order Approve order Prepare parcel Send parcel parcel sent 1 Order [checked] Order [approved] Parcel [prepared] Parcel [sent] - In case of multiple data objects to read, additional definitions are required 83/16/2016
Input Sets
. If an activity has multiple incoming read edges, input sets are used to refine the enabling of that activity · Example: "package parcel" Product [manufactured] Parcel [packed] manufacture product X X package parcel send parcel parcel sent F. obtain product + Product [obtained] Customer address [confirmed] InputSet2 = {Product [obtained] ], Customer address [confirmed]}
Input Sets Refinement
· More concrete - If sequence flow is signaled, the input sets of the activity are evaluated - If an input set is available, the activity is enabled Product [manufactured] Parcel [packed] manufacture product X X package parcel send parcel parcel sent obtain product Product [obtained] Customer address [confirmed] InputSets: InputSet1 = {Product [manufactured], Customer address [confirmed]} 93/16/2016
Output Sets
· If an activity has multiple outgoing write edges, output sets can refine the output of that activity 1 1 Order [received] Order [rejected] Customer information for rejection [created] Check order order received OutputSets: OutputSet1 = {Order [rejected], Customer information for rejection[created]}, Order [accepted] OutputSet2 = {Order[accepted]}
Output Sets Refinement
· More concrete - Output sets refer to a collection of data objects with states, which can be available after the execution of the activity - After activity termination one of the se output sets is available 1 Order [received] Order [rejected] Customer information for rejection [created] Check order order received OutputSets: OutputSet1 = {Order [rejected], Customer information for rejection[created]}, Order [accepted] OutputSet2 = {Order[accepted]} 103/16/2016
Data Objects and Decisions
· Decisions of XOR gateways can use data objects (data-based exclusive gateway) · Example - Decision is based on the state of the Order data object - Check order has two output sets Order [rejected] ed] Reject order Order rejected Check order X Approve order Prep par Order Pa [accepted] Order [checked] [prep
Data Objects and Decisions Formalization
· Decisions might also use values of data objects - Notice that the conditions are not completely formalized - However, the goal of the decision is expressed well in the process model credit_application.amount < 10000 accept credit credit accepted assess credit application (initial) credit application received Credit application assess credit application (advanced) request customer's credit rating credit_application.amount >= 10000 113/16/2016
Data in Processes: Data Storage
· Data storage describes locations where data is stored and retrieved from Send parcel Parcel sent Parcel [sent] 1 Customer data [verified] Transport document [created] Delivery note [created] Warehouse DB CRM System ERP System
Persistent and Transient Data
· Persistent - Data objects are available after the process instance has terminated · Transient - Data objects are created during the process instance and are not available after its termination · In BPMN, all data objects are transient, unless they are - associated with a data storage - data input or data output of a business process Send parcel Parcel sent Parcel [sent] Customer data [verified] Transport document [created] Delivery note [created] Warehouse DB CRM System ERP System 123/16/2016
Activities, Data Objects, States, Systems
Reseller Order Order [rejected] [received] Reject order Order rejected Check order 5 Order received Approve order Prepare parcel Send parcel Parcel sent Reseller .. Order Order [checked] Parcel [prepared] Parcel (sent] Customer data [verified] Transport document [created] Delivery note [created] Warehouse DB CRM System ERP System [accepted] Data Objects and Sub-Processes 133/16/2016
Processing of Data Object Collections
· Idea - Data objects defined as collection can be processed by multiple instances (MI) activities · Input - Each data object of a collection is processed by one activity instance - Parallel or sequential execution possible · Example - Pack order - Parallel execution Pack order Send order = Reseller Order item [accepted] Order item [packed] Order item [sępt]
Processing of Data Object Collections Output
· Output - Each activity instance creates a data object for an output collection · Example - The state of each Order item is changed from accepted to packed by the Pack order MI activity Pack order Send order Reseller Order item [accepted] Order item [packed] Order item [sept] 143/16/2016
Processing of Data Object Collections Input/Output
· Input, output of data object collections - Activities can also process collections of data objects · Example - The Send order activity reads the Order item data collection in state packed and changes the state of each order item to sent Pack order Send order Reseller Order item [accepted] Order item [packed] Order item [sent]
Processing of Data Object Collections Consolidation
· Input / output consolidation - An activity can read a data object collection and create just one output data object · Example: Consolidate order - After termination of the activity instance, a new data object Order in state consolidated is created Consolidate order Reseller Order item [accepted] Order [consolidated] 153/16/2016
Data in Processes and Sub-Processes
· Transfer of the data objects between a sub-process activity and its child process · Approach - Manual assignment of a data object on the process level to a data object on the sub-process level - Use of references · Attention - Assignment of, e.g., Order to Invoice is possible - No consistency check, modeler has the responsibility to preserve consistency · Notice - Data input and data output can also be applied to sub-processes
Context of Data Objects
Handle order + Order [accepted] Order [sent] Reference Reference Pack order Send order Order [accepted] Order [packed] Customer information [verified] Order [sent] 16