Directed Energy Deposition (DED) technology from Unimore University
Slides from Unimore Università Degli Studi Di Modena E Reggio Emilia about Directed Energy Deposition. The Pdf provides definitions, operating principles, benefits, and limitations of DED, an additive manufacturing technique. It also mentions key machine manufacturers and industrial applications in Computer Science for University students.
Ver más9 páginas

Visualiza gratis el PDF completo
Regístrate para acceder al documento completo y transformarlo con la IA.
Vista previa
Directed Energy Deposition Overview
RU UNIVER NS SIS NSIS ET REGIENSIS II75 UNIMORE UNIVERSITÀ DEGLI STUDI DI MODENA E REGGIO EMILIA 25º Ingegneria Modena Dipartimento di Ingegneria "Enzo Ferrari"
Directed Energy Deposition Prof. Elena Bassoli
Definition of Directed Energy Deposition
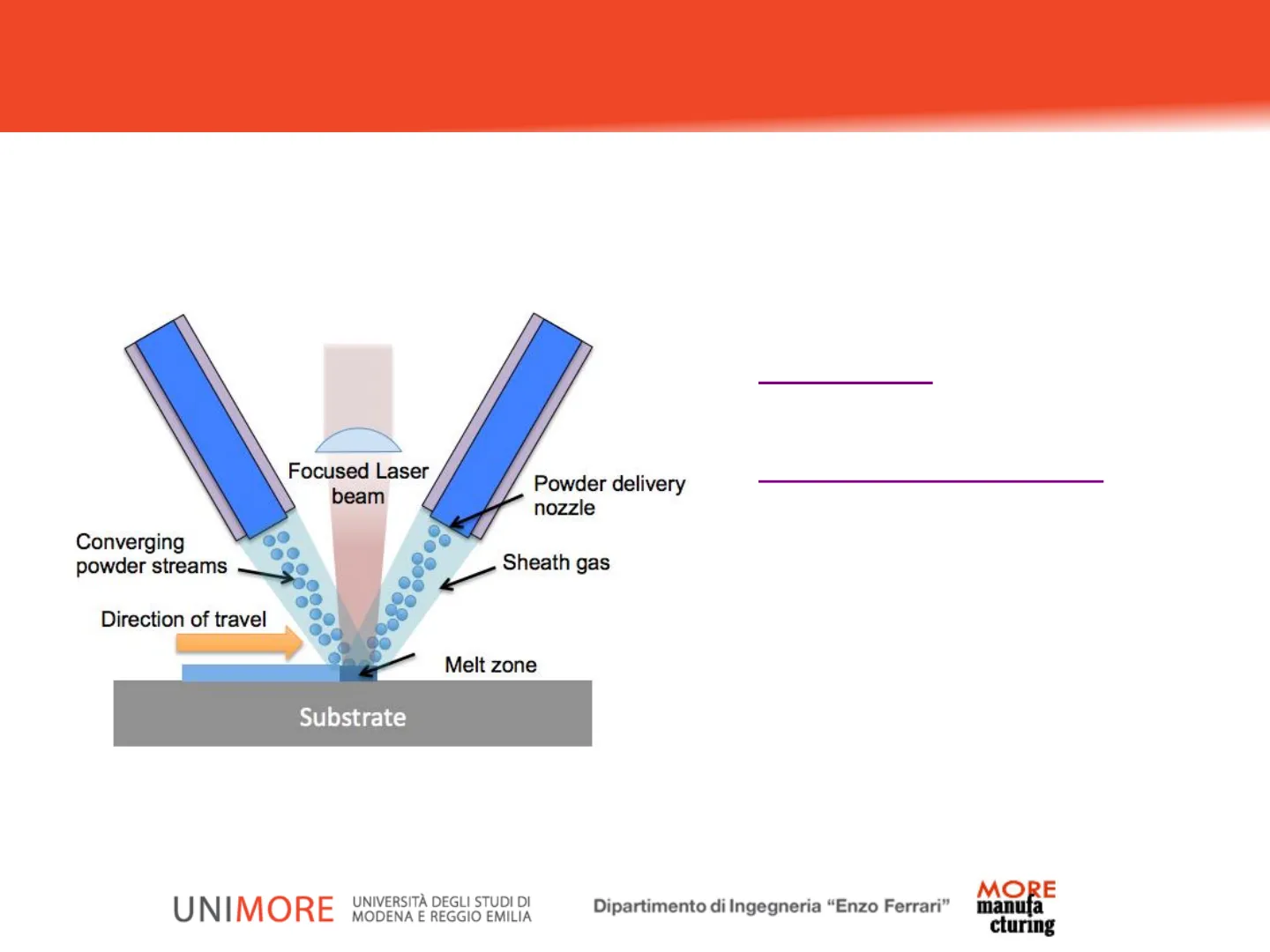
1Definition ASTM Definition: AM process in which focused thermal energy is used to fuse materials by melting as they are being deposited. Video DED Focused Laser beam Powder delivery nozzle Video Hybrid Machine Converging powder streams Sheath gas Direction of travel Melt zone Substrate
Commercial Acronyms for DED
Commercial acronyms: LENS (Laser Engineered Net Shaping), DLF (Directed Light Fabrication), DMD (Direct Metal Deposition), LBMD (Laser-Based Metal Deposition). UNIMORE UNIVERSITÀ DEGLI STUDI DI MODENA E REGGIO EMILIA Dipartimento di Ingegneria "Enzo Ferrari" MORE manuța cturing
Basic Principle of DED Machines
2Basic Principle The machine uses a deposition head that consists of an integrated collection of laser optics, powder nozzle(s) and inert gas tubing which deposits melted material onto the substrate, where it solidifies. The substrate can be either a flat plate on which a new part will be fabricated or an existing part onto which additional geometry will be added. POWDER LASER BEAM CLAD® NOZZLE DEPOSIT UNIMORE UNIVERSITÀ DEGLI STUDI DI MODENA E REGGIO EMILIA Dipartimento di Ingegneria "Enzo Ferrari" MORE manufa cturing
Molten Pool and Control in DED
3Basic Principle In DED, the laser generates a small molten pool (D = 0,25-1 mm, h ~ 0,1- 0,5 mm) on the substrate as powder is injected into the pool. Deposition is controlled by relative differential motion between the substrate and the deposition head that can be accomplished by moving the deposition head or the substrate or both together in 4 or 5 axis systems. The building chamber is filled with Argon in order to reduce oxygen contamination and reactions. UNIMORE UNIVERSITÀ DEGLI STUDI DI MODENA E REGGIO EMILIA Dipartimento di Ingegneria "Enzo Ferrari" MORE manuța cturing
DED Process Parameters
4Process parameters DED machines are sold as flexible platforms, optimum process parameters are material dependent and application/geometry dependent.
Important Process Parameters
- Track scan spacing
- Layer thickness
- Powder feed rate
- Laser traverse speed
- Laser power
- Laser spot size
- Scan pattern
Laser beam Shielding gas Co-axial Powder feeder Shielding gas compresses powder stream All these parameters can be dynamically changed during the building process through sensor feedbacks data, to control deposit thickness and solidification rate. UNIMORE UNIVERSITÀ DEGLI STUDI DI MODENA E REGGIO EMILIA Dipartimento di Ingegneria "Enzo Ferrari" MORE manuța cturing
Materials Used in DED
5Materials Any metal powder or mixture of metal powders which are stable in a molten pool can be used. Generally, metallic materials that exhibit reasonably good weldability are easy to process. Different powders can be delivered in precise amounts to the melt zone using separate feeders to generate various alloys and/or composite materials in-situ or FGM (Functionally Graded Materials). Fig. 9.10 Smooth transition between a 100% Ti-6-4- and 100% Ti-22-23 alloy in the gage section of a tensile bar. The transition region is shown at higher magnification (courtesy Optomec) Ti-6-4 Ti-22-23 DED processes can involve extremely high solidification cooling rates, from 103 to 105 °C/s. This lead to high residual stresses and several microstructural peculiarities including very fine grain size, leading to higher strength. UNIMORE UNIVERSITÀ DEGLI STUDI DI MODENA E REGGIO EMILIA Dipartimento di Ingegneria "Enzo Ferrari" MORE manuța cturing
Benefits and Drawbacks of DED
6Benefits and drawbacks
Limitations of DED
- Poor resolution and surface finish: max accuracy ~ 0,25mm, minimum surface roughness ~ 25um.
- Slow build speed: typical deposition rate 25-40 g/h
Unique Capabilities of DED
- Unparallelled control of microstructure, ability to change material composition and solidification rate;
- Producing of directionally solidified and single crystal structures;
- Capability to effectively repair and refurbish defective and damaged high- technology components such as turbine blades;
- Ability to produce in-situ generated composite and heterogeneous material parts;
- Depositing of thin layers of dense, corrosion resistant and wear resistant material on components to improve performance and lifetime UNIMORE UNIVERSITÀ DEGLI STUDI DI MODENA E REGGIO EMILIA Dipartimento di Ingegneria "Enzo Ferrari" MORE manuța cturing
DED Machines and Manufacturers
7Machines Currently, Optomec® is the main manufacturer of these kind of systems. It provides standalone machines or deposition head modules which can be integrated in pre-existing CNC machines. Optomec LENS 850-R video (page end)
Optomec LENS 850-R Performance Parameters
LENS 850-R Typical Performance Parameters Process Work Envelope 900 x 1500 x 900 mm Enclosure Class I Laser Enclosure, Hermetically sealed to maintain process environment and Safety Motion Control 5-axes standard: XYZ linear gantry motion Tilt-Rotate worktable All axes under full CNC control Positional Accuracy ±.25mm Linear Resolution ± .025 mm Motion Velocity 60 mm/s Deposition Rate Up to 0.5 kg/hr Parts Handling Tilt-Rotate table tilts +/- 90°, infinite rotation. Rails and part cart allow table to move through machine and out. 38 cm diameter antechamber. Gas Purification System Dual unit maintains 02 level continuously ≤ 10 ppm Powder Feeder Two feeders each hold up to 14 kg of powder Lasers 1 or 2 kW IPG Fiber Laser Software G-code Workstation Control; STL Editing; Part- Prep slicing Closed-Loop Controls Optional SMART-AM™ melt pool sensor Enclosure Dimensions 3 x 3 x 3 m w/o gas purification system or laser Also Trumpf® and DMG Mori® provides flexible solutions for hybrid manufacturing UNIMORE UNIVERSITÀ DEGLI STUDI DI MODENA E REGGIO EMILIA Dipartimento di Ingegneria "Enzo Ferrari" MORE manuța cturing
Applications of DED Technology
8Applications Wide applications range:
- Manufacturing
- Hybrid manufacturing (subtractive + additive)
- Functional prototyping
- Materials discovery
- Surface coatings
- Rework and repair
- Welding and joining Laser Metal Deposition UNIMORE UNIVERSITÀ DEGLI STUDI DI MODENA E REGGIO EMILIA Dipartimento di Ingegneria "Enzo Ferrari" MORE manuța cturing 9