Raw Materials - Animal Sources: impatto della crescita demografica sulle risorse
Slide sull'impatto della crescita demografica sulle risorse naturali e la produzione alimentare, con focus sull'allevamento di suini e pollame. Il Pdf, adatto allo studio universitario di Economia, include dati su produzione, consumi e commercio internazionale di carne, con osservazioni di Malthus e fattori limitanti la capacità di carico del pianeta.
Mostra di più66 pagine
Visualizza gratis il Pdf completo
Registrati per accedere all’intero documento e trasformarlo con l’AI.
Anteprima
Materie Prime - Fonti Animali: Introduzione
Oral exam: 3 questions P. Colli 29/02 RAW MATERIALS - AMINAL SOURCES INTRODUCTION The planet is changing. While it took the global population 12 years to grow from 7 to 8 billion, it will take approximately 15 years - until 2037 - for it to reach 9 billion, a sign that the overall growth rate of the global population is slowing. The increase in human population is a concern for the whole Earth because of the possible lack of resources. The distribution of population is uneven and this has an impact on agriculture, because if the density is high there is not enough space for production, there can be competition between the land available for population and the land needed to meet human needs.
We have had exponential growth, especially in the last period. Human population growth -> 33% going from 7.8 to 9.6 billion in 2050. Demand for agro-livestock food products increases by 70% (FAO 2019). Livestock products provide 17% of global food kilocalories and 33% of total protein. Earth overshot day -> date when humanity has exhausted nature's budget for the year. For the rest of the year, we maintain our ecological deficit by drawing on local resource stocks and accumulating carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. We are accumulating a debt relative to the available resources on the planet. We currently live as if we had 1.7 planets at our disposal. Our way of life should change rapidly to avoid worsening this scenario. After 2000 our problems started, in 2020 with covidious people the way of thinking has changed a bit. There will be an increase in population, growth will be concentrated in Asia and Africa, this will also impact the demand for animal products.
Proiezione della Popolazione Mondiale
Projection of world population change over the next 40 years (2050 vs 2011):
- +34% world population;
- +70% food production needed.
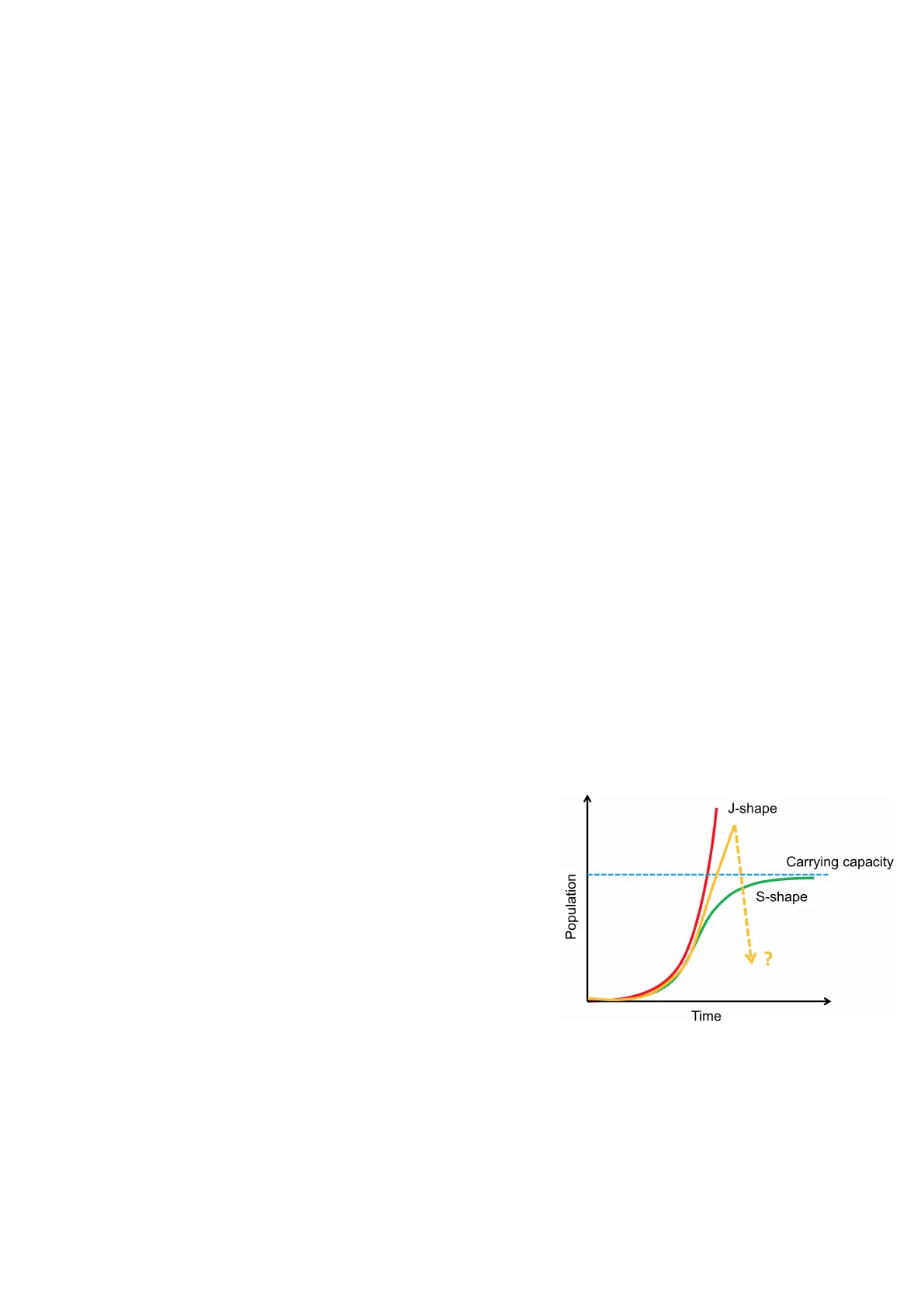
In 1944, 29 reindeer were brought to the island by the USA Coast Guard to provide an emergency food source. The Coast Guard abandoned the island a few years later, leaving the reindeer behind. At first there was a 200-fold exponential growth, then within a few years the population collapsed again as it depleted the island's resources. Another strategy adopted by microorganisms is that mo reach a threshold and then become stable, depending on how much resources are exploited. The carrying capacity indicates the amount of resources that the environment makes abìvìable for the population, if the population stays close to the carrying capacity then it will survive as a mo, otherwise it will perish. Human population -> yellow line; will we continue to grow as we have so far? Probably not, but we must be aware that there will be a theoretical crisis point. As time goes on, population continues to grow exponentially, while food production grows arithmetically, which will lead to a crisis point where population will exceed food.
Modelli di Crescita della Popolazione
J-shape Carrying capacity Population S-shape ? Time
Teoria di Thomas R. Malthus
Thomas R. Malthus -> "An Essay on the Principle of Population as it affects the future improvement of society" in 1798. He analyzed English population during the 18-19 centuries with the Industrial Revolution. A key part of the book was devoted to what is now known as the Malthusian law of population. The theory holds that increasing population rates contribute to increasing labor supply, inevitably lowering wages. In essence, Malthus feared that continued food population growth would lead to poverty.
1P. Colli Malthus' observations: an increase in a nation's food production improved the welfare of the population, but the improvement was temporary because it led to population growth, which in turn restored the original level of per capita production. Humans have a propensity to use abundance for population growth rather than to maintain a high standard of living. Populations tend to grow until the lowest class suffers deprivation, lack and increased susceptibility to war, famine and disease. If we can double the number of food items by changing the industry, we will delay the crisis point. Correct until the 18th century because people were on average very poor and the population was growing. Agriculture was unable to increase its carrying capacity beyond population growth and alleviate poverty.
Limiti della Teoria Malthusiana
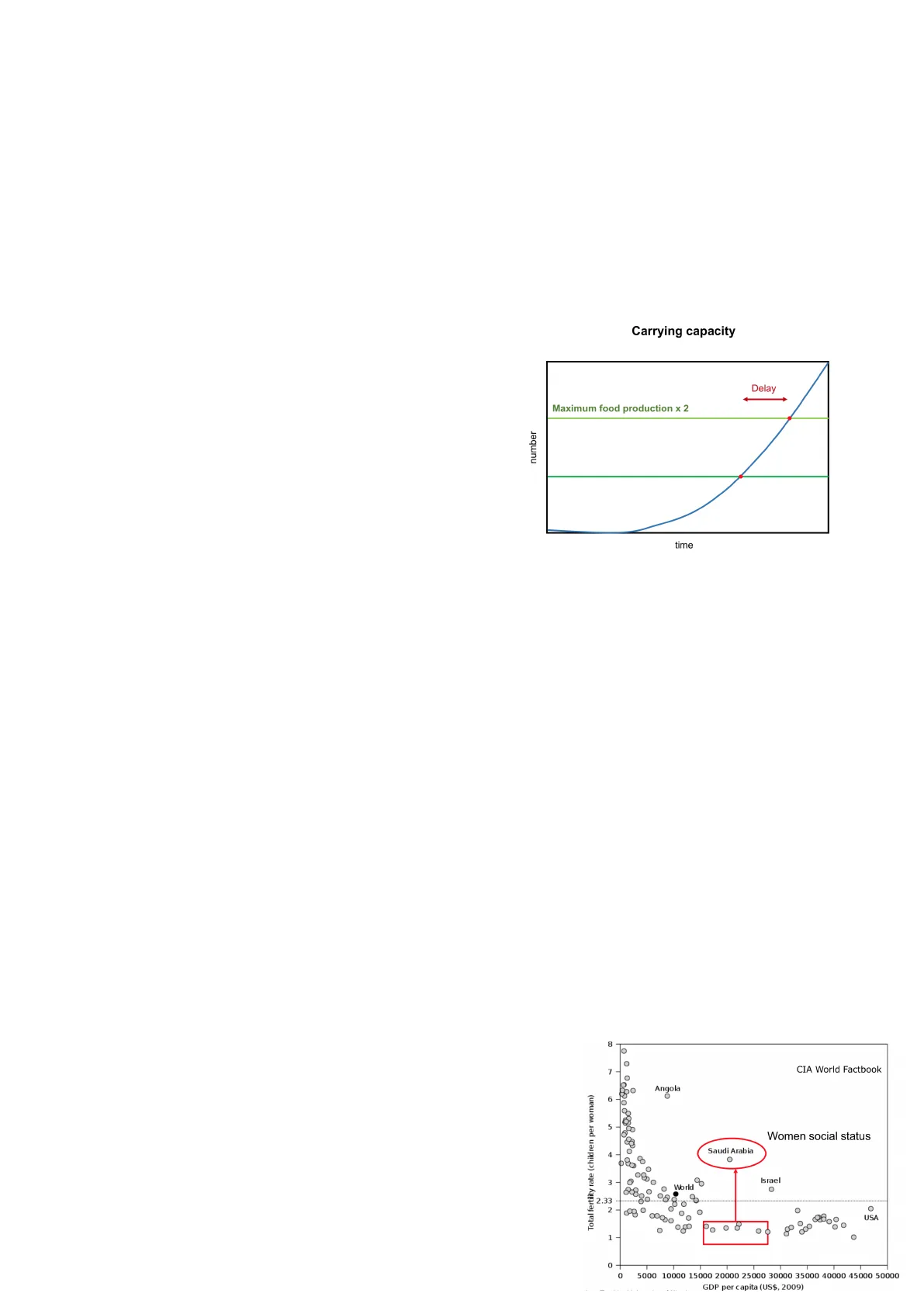
Also, halving the population only delays the problem of crisis, we should change the lifestyle. The population of the UK has continued to grow because the scenario around people keeps changing with the industrial Maximum food production x 2 revolution but also with the green revolution, people started to have more resources and availability. A few number decades ago some scientists re-analyzed some Malthusian claims, saying that in 1970 and 1980 we would face crisis (wrong again !). We need to be aware that even though we now have tools to produce more time efficiently, we need to find new strategies to reduce inequality and build a new society in which everyone can have safe and good quality food.
Fattori Limitanti della Capacità di Carico
Limiting factors in carrying capacity:
Carrying capacity Delay CIA World Factbook Total fertility rate (children per woman) Women social status 2 C USA O 20 O 1 0 0 0 5000 10000 15000 20000 25000 30000 35000 40000 45000 50000 GDP per capita (US$, 2009) Life expectancy -> We need more food if more older people remain on earth, in Italy life expectancy for women (longer than men) is over 80 years. There will be different challenges as communities age because of the different demands that changes in physiology make.
- Water
- Space to live
- Food
- Pollution
- Energy
There are countries with a stable trend, such as Japan and Germany, while others are experiencing population increases, such as Nigeria and Uganda. We can look at the death-nature rate -> we can know how the population will grow (or decrease). If the death rate decreases faster than the birth rate, the population will increase. Scientists assumed there were 4 stages of population growth, after a while the death rate decreased. It took a while for the birth rate to start decreasing (150 years for England), meanwhile the population increased a lot, from 10 to 40 million (depending on the country's level of development). There are areas of the world where half the population is younger (Africa) and other countries where half the population is older (Europe/Italy). There is a correlation between the fertility rate and the average age of the population; there is more fertility in Africa. To achieve balance, each woman should give birth to two children. Some factors 8 related to fertility are health; the lower the cost of domestic 7 product per person, the higher the fertility rate. There are also Angola 6 some countries where this behavior is not followed. We can see 5 a scatter plot and identify the groups that stand out -> 4 00 Saudi Arabia 0 outcomes that may result from measurement error or there could be factors that explain this behavior. 3 Israel World C 2.33 OF CP. Colli 7/03
Piramide della Popolazione e Domanda di Carne
The age of first marriage is also important, and there is also a relationship with the level of education of these women. Another tool to understand what the future demand for meat and these products will be is the population pyramid. On the Y we have the years and on the X the number of individuals:
100+
05-09
95-00
Male
Female
Male
Female
85+
80
75-70
70-74
70-74
70
65-80
60-44
60-44
60
50-54
50
45-
World
45-40
war2
35-
30
25-20
Baby b 2529
20-34
20-2
15-10
15-1
10.50
10-1
0
120 100 80 60 40 20 0
0 20 40 60 80 100120
7.5%
2.5%
2.5%
7.5%
In 1920 the number of new births was far greater than the number of old people. In 40 years, the number of new births has declined; the number of children has declined by a large margin. In Italy the birth rate has changed a lot, this thread is shared by most developed countries. In the beginning the death rate was high, the 16000- 15000 pyramid was shaped like a triangle, now the death rate has 14000- decreased and we will have fewer deaths. Although the human 13000 12000 population will grow, the rate is decreasing. There will be more 11000 10000 people NOT because of an increase in the birth rate, BUT because 9000 8000 people will live longer. 7000 The most likely trajectory is the yellow S-shaped curve. No collapse unless we exceed or have already exceeded the 3000 carrying capacity of the planet. Probably the growth of humans will 2000 1000 slow down a lot and we will approach carrying capacity without touching it (hopefully). Different continents will probably see ESTIMATED IN. HIGH IN. MEDIUM U.N. LOW ACTUAL different changes in population size, we can see that in the EU the population will decrease, while Africa and Asia will see the greatest increase in human population.
Riscaldamento Globale e Produzione Agricola
Global warming -> dairy cows are strongly influenced by outside temperature. During lactation, temperature has a negative impact on milking, as a lot of energy is consumed to keep the animal cool, there are effects on metabolism and oxidative stress, there can also be problems for reproduction, as if fitness is reduced, the chances of having a successful pregnancy are reduced. We may have a change in behavior and an increased chance of being infected by parasites and vectors. If we think about animals in the open space, we may have genetic traits that help vector resistance or ways to not change metabolism etc., which is good, but it is usually unlikely to happen, we are more likely to change breeds that survive the environment better. Greenhouse gases also come from agricultural production (13% of global emissions) and most of them come from energy production. CO2 is part of the carbon cycle; humans release more CO2 into the atmosphere than can be absorbed by the earth. Water is also affected by global warming, in the past it used to rain more frequently with less impact, now there is less water from precipitation and also the distribution over the years. These changes also result in a loss of biodiversity. Human activities compete for available land; land that is likely to be used and exploited will be taken away from the ranges of wild species.Another cause is human choices, e.g., a rancher may change the breed (Frisona produces more than traditional cows).
C O W S 3 MILLIONS OF PEOPLE 6000 5000 4000 10 2.5% 2.9% 5% 7.5% 40-4 40 30-34 Flat st 20 00.04